New 2025 Amazon Premium Shipping Requirements
Amazon’s Premium Shipping program has always driven better conversion rates, improved Buy Box share, and happier customers. But come June 29, 2025, Amazon is rolling out sweeping changes to Premium Shipping performance requirements, and they’re not kidding around. If you’re an ecommerce pro, brand operator, logistics expert, or retail strategist, buckle up. Here’s everything you need to know, served in a conversational style, with a dash of candor, and a sprinkle of “keep-your-cool” honesty.
From Monthly Roll-Ups to Weekly Check-Ins
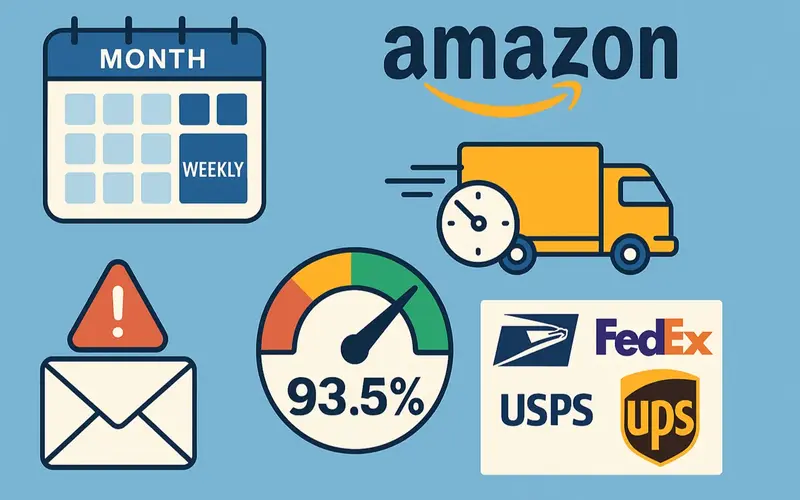
Let’s cut to the chase: under the old system, you needed a 97% on-time delivery rate (OTDR) over a rolling 30-day window to keep that Premium Shipping eligibility. Amazon looked at your performance once a month, sent one warning if OTDR dipped below 97%, and gave you until the next month to fix it. Easy enough—if you had a random bad week, you could smooth it out with stellar performance the rest of the month.
Starting June 29, though, those monthly buffers disappear. Amazon will track OTDR on a weekly basis, from Sunday through Saturday, and drop any Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) orders from that calculation. If your OTDR for Premium Shipping falls below the new minimum, 93.5%, you’ll get your first email warning. Do it again next week, and you’ll receive a second warning. Miss the same threshold three times within four consecutive weeks, and you’re out of Premium Shipping until you earn it back.
Why 93.5%? Amazon’s rationale is that they want customers to experience the same reliability they’ve come to expect from the Prime program. Dropping the requirement from 97% to 93.5% might seem like a concession, but trust me, hitting 93.5% every single week is not easy when you’re dealing with carriers that are out of your direct control.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyWhy This Matters (and Why It’s Tougher Than It Sounds)
No More “Average” Weeks
Under the old model, you could have one sloppy week at, say, 94%, and then three spectacular weeks at 99%, and your overall 30-day OTDR would still be above 97%. Now, if that first week is below 93.5%, you’ll get dinged immediately. A single underperforming week can trigger a warning, and you can’t “erase” it with future weeks once that four-week window closes.
Carriers Need to Be in Your Back Pocket
Amazon explicitly calls out approved carriers like UPS, FedEx, USPS, and OnTrac. If a carrier misses scans, delays pickups, or delivers late, you’re on the hook. The OTDR calculation counts the percentage of orders that arrived on or before the promised “Deliver by” date. If your package is scanned late, or not scanned at all, Amazon assumes it’s going to be late unless an on-time delivery scan is received later. That’s why it’s more important than ever to monitor each carrier’s performance, review their “Last-Mile Delivery” scorecards, and swap out underperformers.
Shipping Settings Automation & OTDR-Protected Labels
Good news: Amazon is offering tools to help you hit your weekly targets. Shipping Settings Automation (SSA) will calculate transit times automatically so your “Deliver by” promises match real-world carrier performance. You still need to set accurate handling times, but SSA can help avoid accidentally over-promising.
Then there’s OTDR protection: if you enable SSA and purchase an OTDR-Protected label through Amazon Buy Shipping, Amazon won’t penalize you for late deliveries as long as the delay is due to factors outside your control. It’s essentially a safety net—except it only applies if you do everything else right (set your handling time properly, buy the right label, and ship on time).
What Sellers Must Do Right Now
1. Audit Your Carriers
- Pull up your Carrier Scorecard in Seller Central each Monday morning.
- Look for patterns: Who’s got the slowest last-mile scans?
- Drop carriers that regularly clock in under 95% weekly on-time scans, because once you hit 93.5%, there’s zero wiggle room.
2. Enable SSA on Every Shipping Template
- Navigate to Shipping Settings → Edit Template → Toggle on Shipping Settings Automation.
- Let Amazon calculate transit times based on carrier data. If you don’t do this, you’re basically flying blind and promising delivery dates you can’t reliably meet.
3. Purchase OTDR-Protected Labels
- Go to Manage Orders → Buy Shipping and look for the shield icon indicating “OTDR Protected.”
- If you use an external tool like Cahoot, make sure it’s integrated and configured to buy the correct labels.
4. Track Your OTDR Like a Hawk
- Check your Account Health → Shipping Performance → On-Time Delivery Rate view, filtered to the “Last 7 Days.”
- Log it in a simple spreadsheet or dashboard; if you’re at 95% on Thursday but have a big FedEx hiccup on Friday, you might dip under 93.5% by Saturday.
5. Prepare an Appeal Template
- If you get that dreaded second warning email, you have two weeks to appeal.
- Your appeal should include:
- Specific orders that caused the miss (order IDs, promised vs. actual dates).
- Evidence that you used SSA and OTDR-Protected labels (screenshots help).
- Steps you’re taking to prevent a repeat (e.g., switching carriers, adjusting handling times).
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPThe Ripple Effects on Your Business
Margin Compression vs. Service Reliability
Yes, spending more on premium carriers or buying OTDR-protected labels adds cost. But losing Premium Shipping can crater your conversion rate, tank your Buy Box percentage, and even affect organic search ranking. You have to run the numbers: maybe offering fewer SKUs with Premium Shipping is cheaper in the long run than risking weekly OTDR failures that affect your sales on your highest-performing SKUs (by being kicked out of the program).
Operations & Inventory Juggling Acts
Keeping enough stock in the “right” warehouses, so carriers aren’t shipping from the opposite coast, matters more than ever. If you sell nationally, you may need multiple fulfillment locations (a 3PL or micro-fulfillment center network). Staggering your replenishment orders (especially around holidays) can prevent stockouts that force you to oversell and then ship late.
Small Sellers vs. Big Sellers
Large brands with multi-warehouse setups and teams dedicated to carrier management can adjust more fluidly. If you’re a one-person operation fulfilling out of your garage, you’ll need to be extra strategic—maybe select just two to three proven carriers and ship as many orders as possible the same day you pick them. The bar is higher now, and patience for shipping errors is slim.
A Few FAQs to Keep You Sane
Q: What happens if a hurricane or blizzard slows down my carrier?
A: If Amazon deems it a “major disruption event,” late deliveries in that region won’t count against your OTDR. But you still need SSA + OTDR-protected labels before the delay. Don’t wait for your messages to start flooding; enable those tools now.
Q: Will this affect Seller Fulfilled Prime?
A: Sort of. SFP has its own stricter OTDR requirements, also on a weekly cadence, but it’s evaluated separately. Just remember, your SFP and Premium Shipping OTDRs are on parallel tracks; a slip in one doesn’t automatically tank the other, but it’s best to nail both.
Q: Can I regain Premium Shipping status after removal?
A: Yes, but you must meet all OTDR requirements for four consecutive weeks after your third infraction (without another miss). It’s basically a “clean slate” window: stay above 93.5% each week for four weeks, and Amazon resets your eligibility for that specific requirement.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkFinal Thoughts: Embrace the Change (or Get Left Behind)
Amazon’s shift from a 30-day OTDR roll-up to a 7-day weekly check is a clear message: if you want to hang with Prime-level sellers, you need rock-solid operational consistency and carrier partnerships. There’s no “coasting” on the back of a stellar month anymore; you have to nail every single week.
Yes, the change feels daunting. Your margins may squeeze, and your team (even if it’s a team of one) will need to revamp processes. But savvy ecommerce pros know adversity breeds opportunity. Rethink your shipping playbook:
- Lean into SSA and OTDR-protected labels.
- Cultivate trusted carrier relationships (and ditch underperformers ASAP).
- Monitor your weekly OTDR like your P&L depends on it (spoiler: it does).
- Build redundancy, FBA hybrid, multi-warehouse, or strategic 3PL partnerships.
Master these moves, and you won’t merely survive—you’ll thrive. Happy selling, and may your weekly OTDR always stay north of 93.5%.
Citations
- Amazon Seller Central – Upcoming changes to Premium Shipping
- Amazon Seller Central – Frequently asked questions about on-time delivery rate (OTDR)

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

Fewer Sellers, Bigger Gains: Seizing Amazon’s Shrinking Competition in 2025
Amazon used to feel like a never-ending battlefield: millions of sellers duking it out for every eyeball. Fast-forward to 2025, and things have quietly shifted. Yes, a ton of new sellers keep signing up—roughly a million a year—but the number of active sellers (those getting at least one review in the past year) has actually fallen from about 2.4 million in 2021 to under 1.9 million in 2025. That’s a 20% drop, and it means there’s more traffic up for grabs per seller. In plain English, the average Amazon seller now gets nearly 31% more visits than four years ago. Cue the confetti for anyone still standing, and some serious sticker shock for those just starting out.
Why the Dip in Active Sellers Matters
Let’s unpack that number: Amazon’s overall traffic has stayed roughly level since 2021, clocking in at around 5 billion visits per month across its global network. But active sellers declined from 2.4 million to 1.9 million between 2021 and 2025. Divide the same or slightly higher traffic by fewer storefronts, and voilà, monthly visits per seller climbed from 2,162 to 2,837. In other words, if you’re still in the game, you’ve got about 31% more potential buyer eyeballs on your listings than your counterparts did a few years back.
That traffic bump isn’t just academic. With Amazon’s revenue surging 36% (from $470 billion in 2021 to $638 billion in 2024), it’s clear the pie is growing even as some sellers fall out. Third‐party sellers, who already sold 56% of units in Q4 2021, pushed their share up to 62% by Q4 2024. Translation: More of a bigger pie is yours for the taking if you can navigate the challenges.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyWhy Sellers Are Fading Out
Okay, so why are fewer “active sellers” sticking around? A few big reasons: rising fees, logistical headaches, and cutthroat price wars.
- Amazon’s Fees Have Ballooned
- In some categories, referral, FBA pick‐and‐pack, and storage fees now gobble up over 50% of a product’s list price.
- Monthly or seasonal storage surcharges and random “reclassification fees” can make it feel like Amazon’s charging you just for breathing.
- The result? Margin erosion that many newcomers can’t stomach.
- Inventory & Case-Management Headaches
- FBA is a blessing until your inventory gets stranded, buried under storage‐fee surcharges, or stuck in removal limbo. Solving these requires hours of back-and-forth with Seller Support.
- Switching to FBM (Fulfilled by Merchant) isn’t a slam dunk either; sourcing reliable carriers, managing returns, and weathering holiday shipping bottlenecks add a new layer of complexity.
- Regulatory & Tariff Unknowns
- Tariff rates have been fluctuating unpredictably, particularly for goods from China or certain apparel categories. A 10% hike overnight can wreck your COGS (cost of goods sold) if you’re unprepared.
- Sales tax laws and cross-border customs rules shift every few quarters. Small sellers risk penalties if they slip up.
- Chinese Seller Dominance
- Chinese merchants make up over half of the top-performing Amazon accounts, often undercutting U.S. sellers with razor-thin margins. It’s tough to compete on price when factory-direct sellers list at rock-bottom rates.
Put those together, and it explains why many hopeful sellers register, list a few products… and then disappear. In fact, more than 60% of the top 10,000 Amazon sellers launched before 2019, proving that experience and staying power are huge advantages.
Why the U.S. Marketplace Still Reigns Supreme
If you’re deciding where to list, the U.S. marketplace is still the gold standard. Sure, places like Saudi Arabia boast 8,228 visits per seller, and South Africa is close behind at 8,065. But those markets simply don’t have the total volume or category breadth of Amazon.com. In the U.S., a niche term like “sourdough starter jar” gets roughly 26,766 monthly searches, compared to 179 in Australia or zero in Saudi Arabia. In other words, niches thrive stateside in a way they can’t elsewhere.
Even better: 73% of U.S. sellers who joined in the past year hit their first sale within 12 months. That’s substantially higher than Germany (38%), the U.K. (32%), or Canada (16%). For new sellers looking for quick validation, the U.S. simply offers the best odds.
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPChallenges to Confront Head-On
More traffic is great, but it doesn’t magically overcome the hurdles. Here’s what you’ll face if you jump into Amazon today:
- Margin Erosion: Even with extra visits, if your fees and COGS leave you with negligible profit per unit, those extra eyeballs won’t matter. Carve out a robust pricing model, know your true landed cost—including tariffs, shipping, Amazon fees, and PPC.
- Inventory Planning: Sell-through rates matter. Overstocking triggers costly storage fees; understocking loses you the Buy Box and lets competitors swoop in. Sophisticated 3PL integrations or tools like Forecastly can help you thread the needle.
- Competitive Pricing & Buy Box Battles: Repricers can help, but they’re not magic. When Chinese sellers aggressively undercut, you risk starting a race to the bottom. Focus on unique value propositions, bundling, subscription offers, or enhanced branding to stand out.
- Regulatory Compliance: Keep up with tariff updates. For instance, electronics gear imported from Asia might incur new duties under a 2025 trade ruling—know it before it blindsides your margin.
- Account Health Vigilance: A single A-to-Z claim or policy violation can drop your seller rating. If you rely on Amazon for 80% of your sales, a suspension can be devastating. Build redundancies: own a Shopify store or diversify into Walmart Marketplace.
How to Capture Your Piece of the (Growing) Pie
1. Lean Into Niche Categories: If you’re selling something ultra-specialized—think artisan beard balm, eco-friendly pet toys, or limited-edition kitchen gadgets—your “competition” pool is smaller. Use tools like Helium 10 to spot emerging micro-niches before they catch fire.
2. Optimize Listings with SEO & Enhanced Content: Keywords matter, but so does conversion. High-res images, 360-degree product videos, and A+ content can take your listing from meh to must-buy. When you’ve got 30% more visits, conversion-rate improvement is pure gold.
3. Strategic PPC & DSP Budgets: With that extra traffic cushion, you might discover that CPCs (cost per click) in your niche are actually lower now due to lighter competition. Run a lean Sponsored Products campaign; if your listing’s solid, you can turn that paid traffic into organic momentum.
4. Leverage Prime & Subscription Models: Products eligible for Prime enjoy a higher click-through rate. If the margin allows, consider bundling or small subscription programs to lock in recurring revenue rather than one-off purchases.
5. Diversify Fulfillment Options: FBA is convenient, but a 3PL (third-party logistics company) hybrid or FBM can be more cost-effective once you hit a certain volume. Free two-day shipping is table stakes; just make sure your margins survive the shipping fees.
6. Plan for International Growth, But Don’t Rush: The data shows 69% of sellers stay confined to one marketplace. If you nail the U.S., expanding later to Canada or Mexico can be a logical next step. But don’t spread inventory too thin across 22+ marketplaces when your U.S. business still has growth levers to pull.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkThe Road Ahead
As Amazon’s marketplace matures, the landscape will keep shifting—new fees might pop up, algorithm tweaks could rearrange SERP rankings, and global trade winds will bring fresh tariff puzzles. But right now, a rare alignment exists: fewer active sellers, steady or growing buyer traffic, and a rising slice of third-party volume. For brands with grit, this means more opportunity if you’re willing to do the heavy lifting.
The parting advice? Amazon’s game has always been about endurance. Weather the headwinds, optimize your listings, master your costs, and don’t be afraid to lean into niche categories—and you might just ride this 30% traffic bump into the kind of scale that felt impossible a few years ago.
Is it crowded? Sure. Is it still worth it? For those who can adapt, absolutely.
Citations
- Marketplace Pulse: Amazon Is Less Competitive Than Four Years Ago
- Marketplace Pulse: U.S. Is Amazon’s Most Beginner-Friendly Marketplace
- Marketplace Pulse: 69% of Amazon Sellers Sell in Just One Marketplace

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

Best 3PL Companies: Why Hiring a Traditional 3PL for Fulfillment Is a Mistake
In this article
 27 minutes
27 minutes
- The Traditional Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Model: How It Works & Why It Falls Short
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network: Key Differentiators
- Side-by-Side Comparison: Traditional 3PL vs. Cahoot
- Product Categories Most Vulnerable to Traditional 3PL Limitations
- Risk Analysis & Mitigation for Each Model
- How Sellers Should Evaluate Fulfillment Options
- Conclusion & Next Steps
- Frequently Asked Questions
Rapidly evolving customer expectations, such as next‐day delivery, free shipping, and impeccable order accuracy, have put immense pressure on ecommerce businesses to optimize their supply chain and fulfillment operations. For years, the conventional wisdom held that outsourcing to one of the best 3PL companies (third-party logistics providers) was the gold standard for reliable delivery services. Yet today, many merchants are discovering that traditional 3PL companies carry hidden costs, limited flexibility, and operational inefficiencies that hinder business growth. In many cases, partnering with a 3PL company is seen as a way to support a business’s growth by streamlining logistics and enabling scalability, but these benefits are not always realized with traditional providers. In contrast, peer-to-peer fulfillment networks, like Cahoot, leverage existing ecommerce expertise, distributed inventory management, and advanced logistics technology to deliver seamless, technology-driven fulfillment services. This article explains why partnering with a traditional 3PL for logistics operations can be a mistake and offers actionable advice on how to evaluate alternatives, with a focus on Cahoot’s assetless, peer-to-peer model.
The Traditional Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Model: How It Works & Why It Falls Short
Third-party logistics companies (3PL) have historically provided comprehensive supply chain solutions: warehouse storage, pick-pack-ship, freight forwarding, reverse logistics, and value-added services such as kitting or custom packaging solutions. These services are part of the broader supply chain management functions that 3PLs handle for their clients, including activities like warehousing, transportation, inventory management, and order fulfillment. 3PLs also offer logistics management as a core service, encompassing warehousing, transportation, and inventory control to streamline and optimize supply chain operations. They often own or lease large fulfillment centers, invest heavily in robust logistics infrastructure, and tout their extensive global network. The logistics capabilities of 3PLs support ecommerce business operations by enabling companies to scale, improve efficiency, and meet customer demands effectively. While these supply chain management services sound appealing in theory, promising operational efficiency and cost savings through economies of scale, in practice, many merchants discover that traditional 3PLs introduce new challenges.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyCentralized Warehousing & Fixed Asset Overhead
Traditional 3PL providers typically own or lease multiple fulfillment centers across regions, relying on a robust network of facilities to support their operations. Their extensive network enables broad geographic reach and scale, investing in forklifts, racking, and extensive staffing for supply chain operations. This means they carry significant fixed asset costs, warehouse rent, utilities, labor, and equipment depreciation that must be recouped through minimum-volume contracts and storage fees. During slow seasons, those costs remain constant, leading 3PL companies to impose strict minimum-monthly invoices or chargeback penalties when order volumes dip.
Actionable Takeaway: Request a fully itemized quote from your 3PL, asking specifically about storage minimums, seasonal surcharges, and long-term lease obligations. If their base overhead drives your logistics costs up regardless of your sales volume, consider alternative models with usage-based pricing.
Standard Operating Culture vs. Seller-Mindset
Employees at a legacy fulfillment center often fulfill orders for dozens or hundreds of different ecommerce businesses. While service-level agreements (SLAs) and performance metrics exist, many 3PL staff “punch a clock” under broad policies rather than taking ownership over specific brands. This lack of ownership can negatively impact the delivery of quality service, leading to less attention to detail and lower customer satisfaction. As a result, packaging may be generic, void fill may be minimal, and handling may prioritize speed over customer satisfaction. In contrast, partner sellers in a peer-to-peer network like Cahoot are ecommerce experts who ship their own orders all day, every day. They treat Cahoot orders with the same care they give their own, using right-size packaging, quality dunnage, and ensuring precise pick-pack accuracy to enhance customer satisfaction and maintain brand reputation.
Actionable Takeaway: Ask your current 3PL to provide photos or video walkthroughs of their order fulfillment workflow, including how they pick, pack, and palletize your merchandise. Compare that to Cahoot’s model, where partner sellers share their own fulfillment processes and quality control protocols. If your 3PL’s service quality feels generic, it’s time to reevaluate.
Contractual Rigidity & Onboarding Timelines
Signing a multi-year contract with one of the best 3PL companies can lock merchants into rigid rate cards, annual volume commitments, and early-termination penalties. These rigid contracts often prevent businesses from accessing scalable solutions that can adapt to changing demand, such as seasonal spikes or rapid growth, and may also limit the availability of tailored solutions for businesses with unique or evolving logistics needs. Moreover, onboarding a new account at a 3PL often takes 4–8 weeks: mapping SKUs into the warehouse management system (WMS), negotiating carrier contracts, and configuring inventory management integrations with your ecommerce platform. Slow ramp-up times delay your time-to-market, making it nearly impossible to pivot quickly for seasonal promotions or unexpected demand spikes.
Actionable Takeaway: Compare your current 3PL’s onboarding timeline to Cahoot’s plug-and-play setup. Cahoot can typically be ready to fulfill orders within a few days without long-term commitments. If your business requires faster time-to-market, a flexible network model will better support supply chain optimization.
Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network: Key Differentiators
Cahoot’s peer-to-peer model transforms traditional logistics by partnering with established ecommerce sellers, businesses that are already shipping their own orders to end customers every day. This cooperative design creates a distributed network of fulfillment centers without the burden of fixed assets, delivering tailored logistics solutions and tailored services that address the specific needs of different businesses. Cahoot’s advanced technology enables optimized logistics processes, enhancing operational efficiency and delivery accuracy while reducing logistics costs and supporting scalable growth.
Assetless, Cooperative Design vs. Legacy Overhead
Unlike traditional 3PL providers that own or lease expensive real estate, Cahoot operates an assetless model: it leverages partner sellers’ excess storage space and fulfillment capacity. These partner sellers maintain their own robust logistics infrastructure for their own brands, temperature-controlled rooms for supplements, secure areas for electronics, and specialized racks for apparel. By tapping into this existing network, Cahoot eliminates the need for merchants to pay for underutilized warehouse space or fixed labor costs. This approach delivers efficient logistics solutions by reducing overhead and maximizing resource utilization. Pricing becomes purely usage-based, reflecting only the actual pick-pack-ship labor and shipping costs without hidden overhead.
Actionable Takeaway: Run a direct cost comparison: request a quote from your 3PL that includes all overhead fees, minimum storage fees, cross-dock charges, and dedicated labor costs. Then request Cahoot’s usage-based rates, which show exactly what you’ll pay per order. Clients routinely confirm that the predicted ROI is indeed achieved. You’ll likely discover 20%–30% cost savings of your own.
Expertise & Quality Mindset of Partner Sellers
Cahoot’s partner sellers are ecommerce experts who ship thousands of orders per week for their own businesses. They care deeply about customer experience and loyalty, continuously optimizing their logistics operations to maximize customer satisfaction and reduce returns. In addition to their expertise, partner sellers can provide specialized services tailored to specific product types or unique business requirements, ensuring custom fulfillment and supply chain solutions. When these same sellers fulfill Cahoot orders, they apply identical rigor: right-size packaging, high-quality void-fill, and precise SKU handling. This level of specialized expertise, combined with Cahoot’s Fulfillment Verification technology, makes it nearly impossible to ship the wrong item to the wrong customer, thus allowing them to claim a 100% fulfillment accuracy rate. The resulting high quality helps merchants qualify for the most rigorous programs, such as Amazon Seller-Fulfilled Prime (SFP), which demands near-perfect fulfillment accuracy and rapid transit times.
Actionable Takeaway: Identify two high-volume SKUs you currently ship via a third-party. Ask the 3PL how they pack and ship those exact SKUs, review box dimensions and dimensional weight, dunnage materials, and packing checklists. Compare that to the size and weight of your SKUs and confirm that you’re not overpaying for shipping using a too-large box vs. using a right-sized box.
Distributed Network for Supply Chain Optimization, Speed & Reliability
Traditional 3PL fulfillment centers typically rely on regional warehouses. If your end customer falls outside the core distribution zone, standard ground shipping can take 3–5 days. In contrast, Cahoot’s distributed network places inventory at partner nodes strategically located near population centers. This enables next-day or two-day delivery to over 95% of U.S. zip codes, even for merchants based in only a few regions. By leveraging this distributed network, Cahoot provides seamless logistics solutions that ensure fast and reliable delivery. Additionally, Cahoot ships six days a week, unlike many 3PLs that only operate Monday through Friday, and offers a later same-day fulfillment cutoff. This flexibility reduces weekend order backlogs, enhances customer experience, and ensures that ecommerce businesses can meet high customer expectations for fast, reliable delivery.
Actionable Takeaway: Map your top 10 zip codes by sales volume and calculate current transit times from your 3PL’s central warehouse(s). Then ask Cahoot to provide average transit times from its nearest location to those same zip codes. If Cahoot offers a two-day improvement on average, you’ll boost customer satisfaction and reduce cart abandonment related to slow shipping.
Plug-and-Play Technology & Real-Time Visibility
Leading 3PL companies offer logistics software that integrates with ecommerce platforms, but many suffer from delayed data (24–48 hour lags) or clunky user interfaces. Cahoot’s technology-driven fulfillment services are built for real-time integration: native connectors for Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon Seller Central, BigCommerce, and more. As soon as an order is placed, the Cahoot dashboard updates inventory levels, routes the order to the optimal node, and displays carrier tracking in real time. This real-time integration enables businesses to address their unique logistics needs more effectively, ensuring that specific requirements and complexities are managed with greater precision. Built-in analytics and supply chain consulting tools help merchants proactively identify stockouts, detect inventory shrinkage, and optimize reorder points, all within a single, intuitive interface.
Actionable Takeaway: Request demo access to both your current 3PL’s portal and Cahoot’s dashboard. Place a sample order and track how quickly each platform updates order status, inventory levels, and shipping confirmations. If Cahoot’s live updates reduce latency and improve decision-making, you’ll gain a competitive advantage.
Side-by-Side Comparison: Traditional 3PL vs. Cahoot
A direct comparison between industry-leading 3PL providers and Cahoot’s peer-to-peer network makes it clear why many merchants choose to switch. While traditional 3PLs offer standard order fulfillment services, Cahoot provides a more innovative and distributed approach, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency in handling diverse ecommerce needs.
When it comes to shipping and delivery, flexible transportation solutions are crucial for meeting customer expectations and ensuring timely, reliable order fulfillment.
Cost Structure & Overhead
- Traditional 3PL Companies:
- Monthly storage fees based on reserved cubic footage or pallet positions; surcharges during peak seasons.
- High minimum monthly invoice requirements.
- Fixed labor costs for pick, pack, and ship; potential overtime fees during surges.
- Additional value-added services (kitting, returns processing, custom packaging) are often billed at premium rates.
- Fulfillment costs can be significant, as traditional 3PLs may charge extra for tailored ecommerce logistics and fulfillment solutions.
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Network:
- No fixed storage minimums, uses partner sellers’ excess capacity, so monthly invoicing matches actual usage.
- Every order is rate-shopped across all carriers and services supported from every location that has inventory in stock and is assigned to ship for the lowest cost identified, eliminating dimensional-weight surprises.
- Value-added services are billed strictly as time and materials, at transparent, market-competitive rates, reflecting actual usage.
- Fulfillment is optimized for ecommerce businesses, reducing costs by streamlining warehousing, distribution, and fulfillment through a flexible (“elastic”) network.
Actionable Takeaway: Build a simple spreadsheet comparing the cost per order (storage + pick/pack + shipping) for both models over a 30-day period. Include any one-time onboarding fees and account management. If Cahoot’s total landed cost per order is at least 15% lower, you stand to save tens of thousands of dollars annually. Note: Cahoot will do the calculations for you.
Fulfillment Speed & Geographic Reach
- Traditional 3PL Providers:
- Centralized fulfillment often results in 3–5 day ground shipping to certain regions, especially if orders ship from a single warehouse.
- Limited weekend operations; orders placed on Fridays may not ship until Monday, delaying delivery and impacting customer satisfaction.
- Peak-season capacity constraints can force overflow to slower carriers or result in shipping delays.
- Cahoot’s Distributed Network:
- Inventory is placed at multiple fulfillment centers (partner nodes) close to end customers, enabling next-day or two-day delivery to 95% of U.S. zip codes.
- Six-day shipping and later same-day shipping cutoff times ensure weekend orders are processed promptly, delivering to your customers faster.
- During peak seasons and when weather negatively impacts the ability for a carrier to move packages through their shipping network, Cahoot dynamically routes orders to partner sellers with available capacity, mitigating bottlenecks and ensuring high on-time delivery rates.
Actionable Takeaway: Identify your top five high-volume zip codes by sales. Compare average transit days from your 3PL’s warehouse(s) to those zip codes versus Cahoot’s nearest nodes. If Cahoot promises a two-day improvement, you’ll decrease order-related support tickets and boost repeat purchase rates.
Scalability & Flexibility
- Traditional 3PL Companies:
- Staffing levels are fixed; adding labor during surges often comes at a high premium.
- Forecasting must be done months in advance; inaccurate forecasts lead to overstock fees or stockouts.
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Model:
- Scales dynamically with demand, and partner sellers adjust capacity in real time.
- Flexible inventory allocation: Merchants can move stock between partner nodes quickly and easily, reducing excess inventory and stockouts in key regions.
Actionable Takeaway: Analyze your last two Black Friday/Cyber Monday seasons. Document the percentage of orders your 3PL delayed or rerouted due to capacity limits. Then request Cahoot’s peak-season performance metrics for similar volumes. If Cahoot processed 100% of orders on time compared to your 3PL’s 90%, the flexibility is clear.
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPQuality Control & Accuracy
- Traditional 3PL Providers:
- Large warehouses lacking the robust technology to handle tens of thousands of SKUs can yield mis-pick rates exceeding 1%.
- Generic packaging solutions may not meet brand standards, resulting in higher damage rates and customer returns.
- Reverse logistics and returns processing may be siloed, leading to delayed refund issuance and negative customer experiences.
- Cahoot’s Partner-Seller Expertise:
- They apply the same high standards, checklists, barcode scanning, and dual verification to Cahoot orders as they do their own, delivering efficient fulfillment services with high accuracy and low error rates. Plus, partner sellers can ONLY ship Cahoot orders using the Cahoot technology. There’s no option otherwise. The technology literally prevents fulfillment defects.
- Specialized partner sellers offer custom solutions such as cold storage, cold pack shipping, food grade storage, FDA registration, FBA Forwarding, oversized SKUs, hazmat, fragile…you name it.
- Integrated reverse logistics network streamlines returns, orders are inspected locally, restocked quickly, and refunds are issued promptly, enhancing customer satisfaction. Plus, Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Returns solution virtually eliminates returns altogether.
Actionable Takeaway: Request fulfillment accuracy reports (mis-pick and damage rates) from your current 3PL for the past six months. Then ask Cahoot for average accuracy metrics across partner nodes. If Cahoot outperforms by at least 0.5%, you’ll see fewer costly re-shipments and better customer reviews.
Product Categories Most Vulnerable to Traditional 3PL Limitations
While every business has unique supply chain requirements, certain product categories tend to suffer disproportionately under the traditional 3PL model. Limitations in traditional 3PLs can disrupt supply chains, leading to inefficiencies and reduced visibility for these products. Cahoot’s peer-to-peer network, with its specialized expertise and distributed infrastructure, addresses these vulnerabilities directly.
Perishable Goods (Food, Supplements)
- Challenges with Traditional 3PL:
- Centralized fulfillment centers may be geographically distant from end customers, increasing transit times and risking spoilage.
- Limited temperature-controlled capacity, 3PL inventory is stored in shared cold rooms, potentially compromising compliance with food safety regulations.
- Ineffective transportation management can further jeopardize the timely and safe delivery of perishable goods, increasing the risk of spoilage.
- Returns or damaged goods due to spoilage create logistical headaches and erode profit margins.
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Advantage:
- Local partner sellers often maintain temperature-controlled facilities near high-demand markets, ensuring same-day or next-day delivery that preserves freshness.
- Specialized sellers follow strict inventory management processes, FIFO (first in, first out), batch tracking, and FDA-compliant storage protocols.
- Reverse logistics for perishable returns are handled promptly, minimizing disposal costs.
Actionable Takeaway: Select two SKUs of perishable goods; compare spoilage or damage rates between your 3PL and Cahoot’s local nodes over a 30-day testing period. The difference in product integrity will be stark.
“Cahoot has amazing technology in addition to their large warehouse network, sort of like Amazon FBA but without the hefty fees or restrictions. Cahoot saved our peak-selling ecommerce season!”
~ Joel Frankel, Fames Chocolates
Speak to a fulfillment expert
Bulky/Oversized Items (Furniture, Fitness Equipment, Home Décor)
- Challenges with Traditional 3PL:
- Central warehouses often rely on national LTL (less-than-truckload) carriers, incurring high dimensional-weight fees and extended transit times.
- Packaging materials may not be optimized for oversized items, leading to damage or higher freight forwarding surcharges.
- Lack of specialized handling can result in higher return rates and frustrated customers.
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Advantage:
- Partner sellers network with regional LTL or white-glove specialists, reducing freight costs and offering more reliable and faster delivery for bulky items.
- Custom packaging solutions, reinforced boxes, corner protectors, and void fill ensure safe transport.
- Flexibility to route orders to the nearest node with capacity, minimizing transit distance and shipping costs.
Actionable Takeaway: Calculate your average dimensional-weight fee for bulky SKUs under your 3PL model. Then request Cahoot’s negotiated regional LTL rates for those same items. If Cahoot reduces freight costs by 20% or more, you’ll see immediate improvement in operational efficiency.
Seasonal Apparel & Flash-Sale Merchandise
- Challenges with Traditional 3PL:
- Requires forecasting inventory levels 3–6 months in advance; inevitable inaccuracies lead to overstock charges or costly stockouts.
- Peak-season storage fees skyrocket, and underutilized space during off-season remains a sunk cost.
- Limited ability to quickly redistribute merchandise across multiple fulfillment centers.
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Advantage:
- No storage minimums; merchants pay only for what they store and ship, eliminating off-season overhead.
- Ability to quickly shift inventory between partner nodes based on real-time demand analytics.
- Network flexibility ensures that flash-sale items are placed close to buyers as soon as sales data emerges, reducing lead times and lowering return rates.
Actionable Takeaway: Analyze your previous two seasonal peaks, quantify days of stockouts and overstock costs under a 3PL model. Then compare to Cahoot’s pilot performance over the same period. If Cahoot reduced stockouts by 30% and eliminated off-season fees, seasonality becomes a strategic advantage.
High-Value Electronics & Luxury Goods
- Challenges with Traditional 3PL:
- Longer transit times increase the risk of theft or damage; generic packaging may not meet premium-brand quality standards.
- Many 3PLs treat high-value SKUs the same as everyday commodity items, leading to higher insurance claims.
- Standard returns processing can be slow, frustrating customers when expensive items need repair or replacement.
- Cahoot’s Peer-to-Peer Advantage:
- Specialized partner sellers can offer dedicated white-glove service and custom secure shipping, ensuring better tracking and handling for luxury items.
- Custom packaging solutions, anti-static bags for electronics, and reinforced packaging for fragile components reflect a brand’s commitment to quality.
- Integrated reverse logistics allow expedited returns, enhancing customer loyalty and reducing potential chargebacks or disputes.
Actionable Takeaway: Track your shrinkage or damage claim rates for high-value SKUs over six months with a traditional 3PL. Then run a small pilot with Cahoot for those same items. If Cahoot’s damage rates decrease significantly, perhaps by over 50%, you’ll safeguard both profit margins and customer satisfaction.
Risk Analysis & Mitigation for Each Model
Every fulfillment decision carries risks. By understanding and quantifying those risks, merchants can make informed choices aligned with supply chain performance goals.
Hidden Fees & Contract Penalties (Traditional 3PL)
- Risks:
- Automatic rate escalators tied to fuel surcharges or annual inflation adjustments.
- Excessive storage charges when inventory dips below or exceeds contract expectations.
- Early termination penalties that can amount to thousands of dollars if you switch providers mid-contract.
- Cahoot’s Mitigation:
- Transparent, usage-based invoicing with no hidden surcharges; each line item (pick/pack, packaging, shipping) is clearly detailed.
- No long-term commitments.
- Dynamic pricing that reflects current market rates for shipping carriers, reducing the risk of unexpected cost spikes.
Actionable Takeaway: Ask your 3PL rep to provide a full 12-month cost breakdown, including all surcharges, storage minimums, and penalty clauses. Then request Cahoot’s itemized quote. If Cahoot’s transparency reduces your logistics costs by 15% or more, the assetless model is clearly superior.
Inventory Management: Shrinkage & Mis-Picks
- Risks (Traditional 3PL):
- Large fulfillment centers handling thousands of SKUs often exhibit mis-pick rates above 1%, leading to returns (lost sales) and re-shipments (lost inventory and lower overall margins).
- Generic security protocols may not deter employee collusion or theft.
- Limited fraud detection software within legacy warehouse management systems (WMS).
- Cahoot’s Mitigation:
- Partner sellers use barcode scanning, dual verification, and built-in fraud detection software to maintain mis-pick rates near 0%.
- Inventory is treated as if it’s their own; partner sellers have a vested interest in reducing shrink, since they rely on the same processes to ship their own products.
- A distributed network reduces the impact of a single node’s shrinkage; issues are localized and resolved quickly.
Actionable Takeaway: Review your 3PL’s last inventory shrinkage report. Then request Cahoot’s average shrinkage metrics. If Cahoot’s partner network consistently demonstrates lower shrink and mis-pick rates, you’ll reduce costly re-shipments and improve customer trust.
Peak-Season Capacity Constraints
- Risks (Traditional 3PL):
- Limited storage and labor capacity during Black Friday/Cyber Monday and other major sale events often leads to delayed orders, oversell situations, or surcharges.
- Forecasting must be done months in advance; inaccurate projections result in expensive last-minute labor or off-site warehousing.
- Manual rerouting may be required when capacity thresholds are breached.
- Cahoot’s Mitigation:
- Dynamic, distributed network with partner sellers that can onboard additional capacity within days, no long-term forecasting required.
- Automated order routing ensures that orders flow to nodes with available capacity, avoiding bottlenecks.
- Real-time analytics highlight potential constraints hours before they occur, allowing preemptive adjustments.
Actionable Takeaway: Compile data on how many orders your 3PL delayed or rerouted during your last two peak seasons. Compare that to Cahoot’s performance metrics for similar volumes. If Cahoot processes over 99% of orders on time versus your 3PL’s 90%, the distributed model mitigates peak risks effectively.
Lack of Customer-Centric Focus
- Risks (Traditional 3PL):
- Employees may lack brand-level context, leading to packing errors or suboptimal customer experiences.
- Generic customer service tools and slow resolution of order issues can harm brand reputation.
- Limited ability to create tailored logistics solutions, returns, custom packaging, or premium unboxing experiences.
- Cahoot’s Mitigation:
- Partner sellers have skin in the game; they ship their own products, so they protect brand reputation, customer loyalty, and lifetime value.
- Cahoot’s integrated customer service tools enable real-time chat and immediate escalation for order issues, reducing resolution time.
- Custom packaging solutions, print-on-demand boxes, branded inserts, or kitting are offered by specialized sellers with experience enhancing the unboxing experience.
Actionable Takeaway: Learn about how Cahoot partner sellers prioritize order quality and customer satisfaction. Compare that cultural mindset to feedback from your existing 3PL’s account manager. If Cahoot’s partner sellers demonstrate deeper brand alignment, you’ll foster stronger customer loyalty.
How Sellers Should Evaluate Fulfillment Options
Choosing the right fulfillment partner requires objective metrics, targeted questions, and a thorough pilot test. For ecommerce businesses, it is crucial to select a partner that understands the unique challenges and requirements of online sellers, offering solutions that support growth and operational efficiency. When evaluating providers, be sure to consider their expertise in ecommerce fulfillment, ensuring they can deliver tailored logistics and warehousing solutions that meet your business needs. Below is a step-by-step guide.
Define Core Metrics Up Front
1. Total Landed Cost Per Order (pick/pack + packaging + shipping + storage)
2. On-Time Delivery Rate (aim for ≥ 99% two-day or next-day success)
3. Order Accuracy (target ≥ 99.7% pick/pack accuracy)
4. Customer Satisfaction (returns rate, net promoter score post-delivery)
5. Supply Chain Performance (inventory turnover, shrinkage, stockout events)
Actionable Takeaway: Create a weighted scorecard with these metrics (e.g., cost 40%, speed 30%, accuracy 20%, satisfaction 10%) to compare providers objectively.
Ask the Right Questions in Your RFP
- “What is your average onboarding time for a midsize merchant (5,000 orders/month)?”
- “Can you guarantee two-day delivery to our top 10 metros six days a week, and what are your cutoff restrictions?”
- “How do you handle specialized logistics services, custom packaging, kitting, or temperature-controlled storage?”
- “What is your mis-pick rate and inventory shrinkage percentage over the past 12 months?”
- “Describe your technology integration: how often is my dashboard updated, and how do you handle returns or reverse logistics?”
- “What are your fees for dimensional-weight shipments, peak-season surcharges, and storage minimums?”
Actionable Takeaway: Compile these questions into an RFP spreadsheet. Assign each answer a score (1–5) to ensure apples-to-apples comparison between prospective 3PL providers and Cahoot.
Run a Two-Week, 10-SKU Pilot
1. Select 10 Representative SKUs: Choose a mix of high volume, high value, bulky, perishable, and seasonal products. This step is especially important for an ecommerce business aiming to optimize its logistics and ensure that fulfillment solutions can support growth and operational needs.
2. Split Shipments: Ship half of those SKUs through your incumbent 3PL and half through Cahoot for 14 days.
3. Measure Key Metrics:
- Total cost per order (including any hidden fees)
- Fulfillment speed (order cutoff to delivery)
- Return handling efficiency (time to refund, restocking accuracy)
- Customer feedback (surveys or NPS scores post-delivery)
- Carrier claim incidents (damages, lost packages, mis-picks)
4. Analyze Results Side-by-Side: Document pilot results in a side-by-side table.
5. Make an Informed Decision: If Cahoot saves ≥ 20% on total cost per order or improves on-time delivery by ≥ 2 days, plan to transition fully within 60 days.
Actionable Takeaway: Schedule your pilot as soon as possible, ideally spanning a weekend, to test Cahoot’s six-day shipping and late cutoff capabilities. Use actual order data to ensure an accurate comparison.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Outsourcing logistics to one of the best 3PL companies once seemed like an easy path to supply chain optimization. Yet traditional 3PLs, with fixed asset overhead, rigid contracts, and a cookie-cutter approach to fulfillment, often burden merchants with hidden fees, slower speeds, and lower service quality. Cahoot’s peer-to-peer fulfillment network, on the other hand, leverages partner sellers’ existing logistics infrastructure, advanced technology integration, and specialized expertise to deliver scalable, tailored logistics solutions that enhance customer satisfaction, reduce logistics costs, and drive business growth.
Immediate Actions for Merchants
1. Build Your RFP Scorecard: Include metrics for cost, speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction, and use it to evaluate your current 3PL and Cahoot side-by-side.
2. Schedule a Two-Week Pilot: Select 10 representative SKUs and ship through both providers to gather real data on costs and performance.
3. Negotiate Exit Clauses: If you’re under contract with a 3PL, review your termination penalties and create a transition plan to minimize fees.
Long-Term Fulfillment Strategy
- Annual Review of Fulfillment Partners: Market dynamics, shipping costs, customer expectations, and technology evolve rapidly. Revisit your fulfillment strategy every 12 months to ensure you remain agile.
- Invest in Technology-Driven Fulfillment Services: Embrace platforms that offer real-time inventory management, automated supply chain optimization, and integrated customer service tools.
- Leverage a Robust Logistics Network: Whether you choose a peer-to-peer model like Cahoot or another 3PL provider, prioritize a distributed, scalable network with specialized expertise in your product category.
By proactively evaluating fulfillment options, considering both traditional 3PL companies and innovative networks like Cahoot, merchants can optimize logistics processes, enhance supply chain performance, and ultimately deliver the best possible customer experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between traditional 3PL companies and Cahoot’s peer-to-peer fulfillment network?
Traditional 3PLs operate large, centralized fulfillment centers they own or lease, carrying significant fixed-asset overhead and often requiring long-term contracts with minimum-volume commitments. Staffing in these warehouses typically fulfills dozens of brands, which can lead to generic packaging, higher mis-pick rates, and slower response times. In contrast, Cahoot partners with established ecommerce sellers who ship their own orders daily. Because these partner sellers treat Cahoot orders like their own, using right-size packaging, quality dunnage, and rigorous inventory management, order accuracy is higher, and customer satisfaction improves. Cahoot’s assetless, distributed model leverages excess capacity across multiple fulfillment centers, resulting in usage-based pricing without hidden storage fees, six-day shipping with a later cutoff, and real-time, technology-driven visibility.
How do logistics costs compare between a traditional 3PL and Cahoot’s model?
With traditional 3PLs, merchants often face minimum monthly storage fees, peak-season surcharges, and dimensional-weight penalties, even when order volumes dip. They also pay a markup on labor for pick/pack services. Cahoot’s peer-to-peer network eliminates fixed storage minimums by using partner sellers’ excess space, so you pay only for what you store and ship. Cahoot’s blended per-order rates include negotiated carrier discounts, reducing transportation costs. In practice, many merchants see 15%–30% lower total landed cost per order with Cahoot because there are no hidden surcharges, and pick/pack labor comes from existing ecommerce experts rather than centralized warehouses with fixed overhead.
Which product categories benefit most from switching away from a traditional 3PL?
Certain categories suffer most under a centralized model:
- Perishable Goods (Food, Supplements): Traditional 3PL warehouses can be far from end customers, increasing transit times and spoilage risk. Cahoot’s local nodes often include partner sellers with temperature-controlled facilities near key markets, ensuring same- or next-day delivery and reducing waste.
- Bulky/Oversized Items (Furniture, Fitness Equipment): Centralized LTL freight lanes incur high dimensional-weight fees and longer transit. Cahoot dynamically matches orders to regional LTL or white-glove carriers, lowering freight costs and improving reliability.
- Seasonal Apparel & Flash-Sale Merchandise: Traditional 3PLs require months of forecasting and charge steep peak-season storage fees. Cahoot can adapt to real-time changes swiftly and redistribute inventory between nodes, avoiding both overstock and stockout situations.
- High-Value Electronics & Luxury Goods: Central fulfillment delays increase theft/damage risk; generic packaging may not meet premium standards. Cahoot’s specialized partner sellers provide custom packaging and secure carrier options, leading to lower damage rates and higher customer satisfaction.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkHow should I evaluate fulfillment options to decide between a traditional 3PL and Cahoot?
Start by defining core metrics such as total landed cost per order (storage + pick/pack + shipping), on-time delivery rate, order accuracy, and customer satisfaction (returns rate or NPS). Build an RFP scorecard where you score each provider on these weighted metrics. Ask targeted questions: onboarding timeline for a midsize merchant, two-day delivery capabilities six days a week, mis-pick and shrinkage rates, technology integration, and real-time reporting, and fees for dimensional-weight or peak-season surcharges. Finally, run a two-week, 10-SKU pilot, splitting those SKUs between your incumbent 3PL and Cahoot, to compare actual costs, delivery speed, return handling, and customer feedback. If Cahoot outperforms on cost or speed, it’s likely the better choice.
What technology and customer-centric features set Cahoot apart from traditional 3PL logistics services?
Many legacy 3PLs offer a portal for inventory management and order tracking, but data often lags 24–48 hours, and interfaces can be clunky. Cahoot’s technology-driven fulfillment services integrate natively with major ecommerce platforms, Shopify, Amazon Seller Central, BigCommerce, and more, providing real-time updates on inventory levels, order routing, and carrier tracking. Cahoot’s dashboard also includes built-in reverse logistics workflows to streamline returns. Because partner sellers are also merchants, they apply a customer-first mindset: they use premium packaging, rigorous quality control, and responsive customer service tools, ensuring every order meets high expectations and enhances brand loyalty.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

How To Choose The Best Faire 3PL For Your Orders
In this article
 16 minutes
16 minutes
- Why Selling on Chewy Is Great for Ecommerce Merchants
- Chewy Case Studies (Brand Success Stories)
- Chewy Seller Onboarding (Step-by-Step)
- Common Pitfalls & Pro Tips for Chewy Sellers
- Faire Program Growth & Updates
- What to Look for in a Faire 3PL
- The Role of Logistics in Customer Satisfaction
- Responsive, Reliable Customer Support
- Experience Working with Faire Sellers
- Top Faire 3PL Companies
- Cahoot: The Best Faire 3PL
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
Faire.com is a global B2B wholesale marketplace that connects independent brands (makers/artisans) with retail store buyers. In Faire’s model, Sellers list products at wholesale prices and fulfill orders themselves from their own warehouse or a 3PL. Orders are usually placed in bulk by retailers (often 1–100 units or more) and shipped via standard freight or parcel carriers to store locations. Faire fulfillment is a specialized service tailored to the needs of brands and retailers on Faire, supporting efficient and reliable wholesale operations.
Faire handles order discovery, promotions, and payments, and provides buyers 60-day net terms and (commonly) free first-order shipping. Sellers can join Faire by application; no invite is strictly required, and they maintain full control of inventory.
To fulfill orders efficiently, many Faire Sellers partner with third-party logistics (3PL) fulfillment providers; these companies specialize in various aspects of order fulfillment, including warehousing, shipping, and inventory management. These 3PL companies integrate with Faire’s API to automatically sync orders, inventory levels, and tracking. As such, the Faire integration streamlines the fulfillment process and ensures accurate order syncing between the Seller’s Faire account and the logistics provider.
Why Selling on Faire Is Great for Ecommerce Merchants
Faire offers a unique platform connecting independent brands with retailers, providing an avenue for ecommerce businesses to expand their wholesale operations. The platform’s user-friendly interface and extensive retailer network make it an attractive option for merchants seeking to grow their customer base. Faire enables ecommerce businesses to efficiently meet increased demand, especially during seasonal peaks or periods of rapid growth. Its features are designed to enhance operational efficiency and deliver a seamless customer experience, helping merchants build loyalty and satisfaction.
Faire Case Studies (Brand Success Stories)
Faire’s own “Stories” highlight numerous brands that grew via the marketplace. Jordan’s Skinny Mixes (specialty beverage brand) launched on Faire in 2020 and saw rapid growth: its first year on Faire brought in over $250,000 in wholesale orders, and by late 2023 it had crossed $10 million in lifetime order volume on the platform. Similarly, Audrey’s Home Decor joined Faire in March 2023 and outpaced expectations: nine months in, their sales on Faire were already 10× their original first-year target. Audrey’s reported that Faire accounted for over 50% of its new customers that year, and enabled them to ship to six different countries (compared to only serving local regions before). These cases illustrate Faire’s ability to connect Sellers with a vast pool of retailers (Faire cites over 50,000 cities globally on its platform) and accelerate brand growth.
Faire Seller Onboarding (Step-by-Step)
1. Create Faire Account: Go to Faire.com and select “Sell on Faire”. Complete the application with your business details. There is no selection committee beyond standard vetting.
2. Submit Product Catalog: Once approved, upload your product catalog. Sellers often fill out a template spreadsheet or use Faire’s web tools to add each SKU (title, wholesale price, retail price, description, category, etc.).
3. Set Terms: In your shop settings, specify minimum order quantities, shipping fees (if any), and country availability. By default, Faire buyers get free first-order shipping; you can opt into Faire’s “Insider” program to subsidize all orders.
4. Inventory & Banking: Connect your bank account for payouts. Enter SKU inventory levels. Faire immediately lists your items on the platform.
5. Begin Receiving Orders: Faire will notify you by email when a retailer places an order. According to reports, most new Sellers receive an order within about a week of going live.
6. Process & Ship Orders: Log into Faire to see the order. You have options to accept the order (and choose a ship date), edit it to backorder some items, or cancel if needed. Usually, you will accept and ship. Package the order, upload tracking in Faire, and mark it shipped. Seller gets paid upon shipment (or can pay a fee to get paid immediately).
Common Pitfalls & Pro Tips for Faire Sellers
Despite its advantages, selling on Faire may present challenges such as managing bulk orders, ensuring timely fulfillment, and maintaining accurate inventory levels to meet retailer expectations and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Underestimating Returns: Faire’s liberal return policy can surprise new Sellers. Retailers can return unsold goods within 60 days, and Faire absorbs this cost. Pitfall: Treating every sale as final. Tip: Anticipate ~10–20% returns, price or package products accordingly, and keep some buffer stock. (Faire will even redistribute returns through its “Maker Market”).
- Shipping Cost Mismanagement: Retailers often expect free or very low shipping, due to Faire’s programs. Tip: If shipping costs are high, consider joining Faire Insider (monthly fee) so you subsidize free shipping, or negotiate lower carrier rates via a 3PL. Understanding shipping rates is crucial, as 3PLs can help negotiate better rates and offer cost savings through consolidated shipments and expert management. For heavy or fragile items, charge a reasonable shipping fee through Faire’s checkout instead of absorbing all costs.
- Slow Turnaround: Late shipments can frustrate retailers. Pitfall: Taking longer than promised. Tip: Set realistic lead times (e.g., “Ships in 2 days”), and ship on time or early. Many Sellers find using a 3PL (which processes orders quickly) improves speed and accuracy.
- Inventory Errors: Overselling due to inventory lag leads to cancellations. Tip: Integrate inventory in real time (Faire’s API or 3PL integration). Maintaining order accuracy is essential to avoid cancellations and ensure retailer satisfaction. If an order comes in that you can’t fully supply, use Faire’s “Edit” feature to backorder specific items or quantities instead of canceling the entire order. That way, you still capture part of the sale.
- Poor Packaging: Because orders ship in bulk, insufficient packaging can cause damage. Pitfall: Reusing light consumer boxes. Tip: Use sturdy cartons or pallets for bulk orders. Shipping products in bulk to retailers has unique requirements, so ensure packaging meets wholesale standards. Include a clear packing list and your invoice in each carton. Branding or thank-you notes (allowed by Faire) can impress retailers.
- Ignoring Faire Tools: Faire offers promotions (free shipping codes, newsletter features) and integration tools. Tip: Link your ecommerce site via “Open with Faire” to drive additional sales, and respond to Faire’s periodic buying events or discount opportunities to boost visibility.
- Not Leveraging Data: Retailers value reviews and sales rank on Faire. Pitfall: Listing products and never optimizing. Tip: Refresh products seasonally, add new SKUs often, and encourage retailers to leave reviews (Faire automatically surveys buyers). Sellers may have unique requirements for analytics and reporting to optimize their operations. Engaging in Faire’s marketing (e.g., ads, “New Maker” features) can accelerate growth.
Faire Program Growth & Updates
Faire has grown into a very large ecosystem. Faire reports ~700,000 retail buyers and over 100,000 independent brands active on their platform, and the business is valued at nearly $13 billion. Major publishers like Simon & Schuster have noted selling to ~5,000 stores via Faire, demonstrating its scale. Faire itself has launched new initiatives (e.g., “Faire Insider” buyer program, educational content for retailers) to increase order volume. As order volume grows, managing fluctuations in demand requires robust supply chain management to ensure efficient fulfillment and delivery. The case studies above (e.g., Audrey’s international sales expansion) reflect Faire’s broad reach: the platform serves retailers in “more than 50,000 global cities”. To support global expansion and efficient fulfillment, Faire’s platform and its partners must meet specific requirements, such as adequate warehouse space and experience with various product types. In sum, Faire’s continual fundraising and technology rollouts (API integrations, fulfillment partners, global expansion) underscore that its 3PL-friendly marketplace is active and scaling rapidly, with a focus on supply chain optimization.
What to Look for in a Faire 3PL
Key considerations when choosing a 3PL for Faire orders include:
- Advanced Inventory Management Systems: Ensure the 3PL offers real-time inventory tracking to prevent stockouts and overselling.
- Seamless Order Fulfillment: The ability to process and ship orders efficiently is crucial for maintaining retailer relationships.
- Transparent Pricing: Look for partners with clear pricing structures to avoid hidden fees that can impact your profit margins.
- Qualities of an Ideal Partner: Select a partner with experience in Faire fulfillment, strong technology integration, and excellent customer service to meet your business needs.
- Value-Added Services: Consider 3PLs that provide value-added services such as kitting, custom packaging, or other specialized solutions to enhance supply chain efficiency.
- Greater Customer Satisfaction: Choosing the right 3PL can lead to greater customer satisfaction by improving order accuracy, reducing errors, and enhancing the overall customer experience.
The Role of Logistics in Customer Satisfaction
Effective logistics play a pivotal role in enhancing customer satisfaction by directly impacting the overall customer experience. Efficient handling of orders, timely deliveries, and responsive support contribute to a positive experience for retailers, encouraging repeat business and fostering long-term partnerships. Additionally, efficiency in logistics operations leads to improved outcomes for both retailers and brands, supporting business growth and higher levels of customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Working with a 3PL
Working with a 3PL offers several advantages:
- Scalable Solutions: A capable 3PL works closely with its clients to address various aspects of logistics and fulfillment, adapting to your business’s growth and managing increased order volumes without compromising service quality. They also work closely with shipping carriers to ensure timely deliveries and reduce delays.
- Operational Excellence: Expertise in fulfillment operations ensures accurate order processing and efficient shipping.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Outsourcing logistics allows you to concentrate on product development and marketing strategies.
Responsive, Reliable Customer Support

Order fulfillment is a complex operation, involving multiple, intricate steps in the process from click to delivery. Things don’t always go as planned, but what is crucial is ensuring that your 3PL has a responsive, reliable customer support team that you can rely on to fix problems fast, with minimal disruption to your business operations.
Experience Working with Faire Sellers
Most traditional 3PLs may not have personnel with the experience and expertise working with Faire to troubleshoot and fix problems fast, costing you precious time and sales. It is important to identify a Faire fulfillment partner with a reliable, responsive customer support team who will be ready to dive in and solve problems quickly, so that you’re always selling and keeping your customers happy.
Here’s what one of our customers had to say about Cahoot’s Support team:
“Cahoot is very responsive and organized in all aspects. Everything is prepared to give anyone the best experience ever. They’re the right partner to help you accomplish your business purpose.”
~ Italian Food Online Store
Speak to a fulfillment expert
So now that we’ve taken a look at the important criteria that guide your choice of a 3PL to support your Faire orders, let’s look at the options that are actually available to you, and the pros and cons of each of them.
Top Faire 3PL Companies
Amazon Multi-Channel Fulfillment
Amazon Multi-Channel Fulfillment (MCF) is Amazon’s outsourced fulfillment service for merchants selling on non-Amazon sales channels, such as Faire, whereby Amazon handles the picking, packing, and shipping of the orders coming from those sales channels.
Ecommerce Sellers can store their inventory at Amazon’s warehouses, and MCF will fulfill the non-Amazon orders from select channels. MCF deploys the same infrastructure and resources that power Amazon’s in-house Fulfilled By Amazon (FBA) logistics network. Sellers seeking FBA alternatives may explore other fulfillment providers.
ShipBob
ShipBob is a 3PL that focuses on serving ecommerce merchants. They have a nationwide network of order order fulfillment centers that enable fast shipping, but they charge extra for guaranteed 2-day shipping. Built for ecommerce, they have an easy-to-use shipping shipping software and a large set of pre-built integrations.
Cahoot: The Best Faire 3PL
Cahoot emerges as a leading 3PL provider for Faire merchants, supporting its clients with specialized Faire fulfillment services tailored to the unique requirements of the Faire marketplace. Their advanced technology integration, real-time inventory management, and commitment to operational excellence ensure seamless and efficient Faire order fulfillment. Cahoot’s Faire fulfillment services are designed for efficiency and accuracy, helping brands meet the unique needs of the Faire marketplace. By partnering with Cahoot, ecommerce businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, streamline their fulfillment processes, and focus on scaling their operations effectively.
Summary
Faire’s wholesale marketplace connects independent retailers with creative brands, offering huge growth opportunities for ecommerce businesses. But with that growth comes new demands for inventory management, order fulfillment, and consistent customer satisfaction. Integrating with Faire’s platform streamlines the supply chain and improves efficiency by enabling seamless order processing, inventory synchronization, and optimized fulfillment workflows tailored to Faire’s requirements. Choosing the right 3PL for Faire orders, one that ensures advanced inventory management systems, seamless order fulfillment, and transparent pricing, can make all the difference in meeting retailer expectations and driving repeat business. Cahoot’s Faire 3PL fulfillment services combine the best of technology and human expertise to help you stand out on Faire’s platform and grow sustainably.
Table 1. Summary of the Faire Marketplace Requirements
|
Requirement
|
Faire Wholesale Marketplace Details
|
|---|---|
|
Access/Application
|
Applications are accepted on Faire.com for brands (makers, artisans, distributors). Faire reviews new Seller applications in the order received. Once approved, Sellers set up a Faire shop by uploading their catalog. There is no listing fee to join.
|
|
Fees & Commission
|
Commission: Faire’s standard commission is 15% on reorder sales (after the first order). For a buyer’s first order from a new shop, Faire charges a higher one-time commission (typically 25%). (These fees are automatically deducted from Seller payouts.)
|
|
Payment Terms
|
Faire funds sales on net-30 terms by default. Retailers typically have 60-day credit terms with Faire, but Sellers are paid as soon as they ship goods (payout initiated upon marking the order as shipped). Sellers may pay a small fee (≈3%) to expedite payment. Faire guarantees payment to the Seller even if the buyer defaults.
|
|
Integration/API
|
Optional but recommended: Many Sellers integrate their systems or 3PL with Faire’s API. Third-party 3PLs (e.g., Cahoot) offer seamless integration, automatically syncing orders, inventory, and tracking with Faire. Otherwise, Sellers can manually manage orders via Faire’s web interface. Faire also offers a Shopify integration app for online Sellers.
|
|
Product Requirements
|
Sellers must upload product listings with high-quality images and descriptions. Faire’s listing interface guides Sellers on categories and tagging. Inventory must be updated promptly. Faire has automated “Maker Tools,” but no strict image/size rules are publicly enforced beyond general ecommerce best practices.
|
|
Shipping Expectations
|
Sellers ship accepted orders within the promised lead time (often 1–3 business days to pick/pack). Retailers expect standard ground or LTL freight shipping (Faire covers free shipping to retailers for “Insider” members, otherwise, Sellers can charge a shipping fee via Faire’s checkout). Shipping carriers commonly include UPS, FedEx, USPS, etc. (the key is reliability). Sellers must upload tracking numbers in the Faire portal for each shipment. 3PL partners typically automate this via API.
|
|
Packing & Labels
|
Each wholesale shipment should include: a packing slip (detailing SKUs and quantities), Seller’s branding (optional), and any required documentation (e.g., invoices, MSDS if applicable). Faire buyers appreciate bulk packaging (e.g., shipping cases with inner-packed units). Sellers should ensure products are well-protected for freight transit.
|
|
Returns/Customer Service
|
Faire offers free returns for retailers up to 60 days after delivery (first return window for each order). Faire handles the return logistics on behalf of Sellers (returns are either credited or redistributed via Faire’s Maker Market). Sellers generally do not pay return shipping and do not take back inventory unless Faire explicitly notifies them. Customer service (order cancellations, questions) is conducted through Faire’s platform; Faire mediates disputes, crediting Sellers or buyers as needed.
|
|
Fulfillment SLAs
|
Faire’s official SLAs encourage fast turnaround (often shipping within 1–2 days for in-stock items). 3PLs serving Faire Sellers advertise “fast & accurate” processing to meet retailer expectations. Sellers must honor lead times set on their Faire profile, or order cancellations may occur.
|
|
Seller Support/Tools
|
Faire provides a dedicated brand dashboard (orders, sales analytics, messaging). Sellers can edit orders (e.g., backorder or cancel items) as needed through the portal. Faire also offers optional services like the “Open with Faire” widget (for DTC sales) and promotions via newsletters or ads, though participation is optional.
|
If you’d like to find out how Cahoot can help your ecommerce business, please get in touch with us. We can’t wait to show you how Faire order fulfillment was meant to be.
If you are selling on multiple sales channels and are interested in 3PLs that can help you with fulfillment, check out our other articles:
1. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Your Shopify Store
2. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Your Macy’s Orders
3. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Target Plus
4. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Wayfair
5. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Nordstrom
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Faire a great opportunity for wholesale ecommerce?
Faire’s massive retailer network and curated marketplace help brands quickly scale their wholesale business and reach new markets.
What challenges do Sellers face when fulfilling Faire orders?
Faire Sellers must manage bulk orders, maintain accurate inventory, and ensure timely shipping to keep independent retailers happy and coming back for more.
What should I look for in a Faire 3PL?
Prioritize advanced inventory management systems, seamless order processing, transparent pricing (no hidden fees!), and proven experience with wholesale fulfillment.
Why is logistics so critical for Faire?
Retailer trust and repeat business hinge on smooth, accurate fulfillment—if orders arrive late or incomplete, retailers won’t hesitate to find a new supplier.
How does Cahoot support Faire businesses?
Cahoot offers Faire-specific 3PL services that ensure operational excellence, real-time inventory tracking, and seamless integration with Faire’s platform, empowering brands to keep retailers delighted and orders flowing smoothly.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

How To Choose The Best Chewy 3PL For Your Orders
In this article
 16 minutes
16 minutes
- Why Selling on Chewy Is Great for Ecommerce Merchants
- Chewy Case Studies (Brand Success Stories)
- Chewy Seller Onboarding (Step-by-Step)
- Common Pitfalls & Pro Tips for Chewy Sellers
- Chewy Program Growth & Updates
- What to Look for in a Chewy 3PL
- The Role of Logistics in Customer Satisfaction
- Responsive, Reliable Customer Support
- Top Chewy 3PL Companies
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
Chewy is a leading online pet retailer that recently launched a curated marketplace allowing select third-party brands to sell via drop-shipping. Under this program, vendors list products on Chewy.com but fulfill orders from their own warehouse or a 3PL, shipping directly to consumers. 3PLs play a crucial role in managing order fulfillment as part of the overall supply chain for Chewy Sellers, handling everything from receiving goods to delivering finished products and managing returns. Chewy partners with a commerce platform (Rithum Commerce Suite) to manage these unowned-inventory sales. In mid-2023, Chewy reported working with over 3,500 brands (110,000+ products) through this model. Enrollment is typically invitation-only: Chewy category managers reach out to qualified vendors (often pet-product manufacturers) and guide them through the Vendor Partner Portal (VPP) onboarding. Once approved, Sellers integrate via EDI/API with Chewy’s system (commonly using Rithum’s DSCO platform), which is compatible with various ecommerce and ERP platforms, to synchronize inventory, orders, shipping, and invoicing.
Why Selling on Chewy Is Great for Ecommerce Merchants
Chewy has emerged as a leading pet supply retailer, offering a vast platform for merchants to reach dedicated pet owners. One key benefit for merchants is the ability to connect with customers who are ready to spend money on pet food, food, and other pet products, driving increased sales and revenue. With its user-friendly interface and loyal customer base, Chewy provides an excellent opportunity for businesses to increase sales and expand into new markets. Chewy’s platform is especially effective for brands selling pet food and related food products, as customers are eager to spend money on these essentials.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyChewy Case Studies (Brand Success Stories)
Although still relatively new, Chewy’s marketplace has attracted prominent pet brands. For example, BARK, Inc. announced in August 2024 that it had launched its bestselling toy collections on Chewy, expanding its product lines available to over 20 million Chewy customers. This partnership is described as the first time Chewy carries BARK toys, indicating Chewy’s effort to broaden its assortment with popular brands. Other pet companies have begun testing Chewy’s platform; for instance, BARK’s entry underscores rapid adoption by leading pet vendors. These brands have scaled their operations to handle the increased order volume generated by Chewy’s large customer base, demonstrating their ability to manage high volume efficiently. Chewy’s Pet Vet “Practice Hub” program, launched in 2021, also illustrates the company’s move to partner with third-party Sellers, though that program is targeted to veterinary clinics rather than general consumer brands. These examples suggest Chewy’s third-party channel is actively expanding, though detailed performance metrics per brand are not yet public.
Chewy Seller Onboarding (Step-by-Step)
1. Invitation/Account Creation: Chewy invites you via email to register on the Vendor Partner Portal. Click the link and create a VPP account.
2. Company & Contact Info: Log in to VPP and complete the Company Information and primary contact fields. This data is often prefilled by Chewy’s merchant team, but you must review and complete any missing details.
3. Skip Ordering (Drop-Ship): In “Ordering Information,” you would normally enter your warehouse locations and lead times, but drop-ship vendors skip this step (Chewy handles orders without requiring vendor stock in Chewy’s DCs).
4. Banking & Tax: Provide banking details (voided check or bank letter) for payments, plus contacts for Accounts Payable and Receivable. Fill out tax forms (W-9, etc.) as prompted.
5. Product Catalog (PAF): Download Chewy’s Product Addition Form (PAF) template from VPP. Enter your catalog data (item names, UPCs, dimensions, pricing, etc.) into the appropriate category sheet, then upload the completed PAF back to VPP.
6. E-Sign Documents: VPP integrates with DocuSign. Review and electronically sign all required vendor agreements and compliance documents.
7. Submit for Review: Once all forms are complete, click “Submit” in VPP. The screen will confirm receipt. Chewy’s team will then review your submission.
8. Integration Testing: After approval, you’ll work with Chewy (via DSCO/EDI or API) to test order flow. Chewy may send sample orders and require successful acknowledgment, shipment, and invoicing.
9. Go Live: After passing tests, Chewy grants you live selling access. Your products will appear on Chewy.com, and actual consumer orders will begin.
Note: Throughout onboarding, focus on building a strong relationship with Chewy’s merchant team. A positive relationship helps ensure smooth onboarding, ongoing support, and long-term operational success.
Common Pitfalls & Pro Tips for Chewy Sellers
While Chewy offers significant advantages, merchants may encounter challenges such as strict fulfillment requirements, managing inventory across multiple channels, and ensuring timely deliveries to maintain customer satisfaction. Third-party logistics providers can help Chewy Sellers by managing the entire logistics process, including storage, fulfillment, and distribution, to streamline operations and meet Chewy’s high standards.
- Missed Integration/EDI Errors: Failing to set up correct EDI/API connections can delay orders. Many retailers rely on robust integration to streamline order processing and maintain efficient B2B exchanges. Tip: Use a middleware or work closely with Rithum/DSCO support to ensure your EDI maps (850/856/810) meet Chewy’s specs. Test end-to-end early.
- Packaging Slip Confusion: Including a generic pack slip can confuse Chewy’s system. Tip: Follow Chewy’s instructions: “Chewy does not use pack slips for drop-ship orders.” Instead, include only a retailer-facing packing list if needed.
- Unsupported Addresses: Shipments to P.O. boxes or military APO/FPO addresses will be rejected. Tip: Validate all customer addresses before shipping; use commercial addresses.
- Slow Fulfillment: Late shipments hurt your vendor rating. Tip: Chewy demands fast fulfillment (often same-day pick, 1–3 days transit for essentials such as pet food, and 1–5 days transit for non-essential, heavy, or specialized items). Keep inventory ready and use overnight/2-day carriers when needed to meet Chewy’s SLA.
- Inventory Sync Errors: Selling out-of-stock items causes cancellations. Effective warehousing is crucial for maintaining accurate stock levels and preventing overselling. Tip: Update your inventory feed or buffer stock to maintain 98–99% in-stock rates. Have a system to quickly edit or cancel orders if you genuinely can’t supply an item.
- Quality/Image Issues: Chewy may reject listings with poor images or missing data. Tip: Provide high-resolution product images and complete descriptions per Chewy’s photo and content guidelines (detailed in VPP playbook).
- Communication Gaps: Delayed responses to Chewy inquiries can stall your onboarding. Tip: Monitor the VPP “Inbox” for Chewy messages and respond promptly. Build a point of contact on Chewy’s merchandising team.
- Pricing Missteps: Avoid setting retail prices too low; Chewy expects competitive but realistic pricing. Tip: Factor in Chewy’s customer base when pricing, and negotiate any MAP policies directly with Chewy’s buyer if needed.
- Return Confusion: Unlike consumer marketplaces, Chewy processes returns centrally. Tip: Understand that Chewy “does not take title to refunded items unless returned,” meaning they may not send items back to you. Clarify return instructions with Chewy for any returns that must be shipped back.
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPChewy Program Growth & Updates
Chewy’s third-party marketplace is rapidly developing. Rising customer demand has driven Chewy’s investment in expanding its fulfillment capacity, with a focus on increasing shipping capacity and improving delivery performance through automation and transportation initiatives. In 2023, Chewy extended its Rithum partnership to expand drop-ship capabilities. According to Rithum, Chewy’s partner network already included 3,500+ brands and 110,000+ products as of mid-2023. Chewy’s logistics infrastructure, including Chewy Freight Services, supports these scaling efforts and helps handle higher order volumes efficiently. Press coverage (e.g., BARK’s August 2024 announcement) and trade articles highlight new brand launches on Chewy, indicating the program is active. Chewy’s financial filings do not break out marketplace revenue, but analysts note Chewy is emphasizing third-party growth alongside its core retail business. Future validation may come from Seller testimonials or Chewy statements; for now, the launch of flagship brands on the platform is a key indicator of momentum.
What to Look for in a Chewy 3PL
When selecting a 3PL for Chewy orders, consider the following:
- Seamless Integration: Ensure the 3PL can integrate smoothly with Chewy’s platform for real-time inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Automated Fulfillment Center: Look for partners with an automated fulfillment center that uses advanced automation to handle high order volumes efficiently. Automation reduces the need for manual heavy lifts, improving safety and boosting productivity.
- Customized Packaging and Value-Added Services: Choose a 3PL that offers value-added services such as customized packaging solutions, aligning with Chewy’s standards and enhancing the customer experience.
The Role of Logistics in Customer Satisfaction
Efficient logistics are crucial in maintaining customer satisfaction. Accurate order fulfillment, timely deliveries, and responsive customer service contribute to a positive customer experience, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
Benefits of Working with a 3PL
Partnering with a 3PL offers numerous benefits:
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes and advanced technologies improve order accuracy and reduce shipping times.
- Cost Savings: Outsourcing fulfillment can lower fixed costs associated with maintaining your own warehouse and staff.
- Scalability: A reliable 3PL can adapt to your business’s growth, handling increased order volumes seamlessly.
- Comprehensive Fulfillment Package: Leveraging a complete fulfillment package from a 3PL can further streamline operations and improve scalability.
Responsive, Reliable Customer Support

Order fulfillment is a complex operation, involving multiple, intricate steps in the process from click to delivery. Things don’t always go as planned, but what is crucial is ensuring that your 3PL has a responsive, reliable customer support team that you can rely on to fix problems fast, with minimal disruption to your business operations.
Experience Working with Chewy Sellers
Most traditional 3PLs may not have personnel with the experience and expertise working with Chewy to troubleshoot and fix problems fast, costing you precious time and sales. It is important to identify a Chewy fulfillment partner with a reliable, responsive customer support team who will be ready to dive in and solve problems quickly, so that you’re always selling and keeping your customers happy.
Here’s what one of our customers had to say about Cahoot’s Support team:
“Cahoot’s support is prompt and personal, not monolithic and apathetic as some large companies tend to be. Cahoot is not only a great 3PL provider but also a strategic partner that goes above and beyond for its clients. They are a 5-star team of people who make it their business to care about yours.”
~ VERSACART
Speak to a fulfillment expert
So now that we’ve taken a look at the important criteria that guide your choice of a 3PL to support your Chewy orders, let’s look at the options that are actually available to you, and the pros and cons of each of them.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkTop Chewy 3PL Companies
Amazon Multi-Channel Fulfillment
Amazon Multi-Channel Fulfillment (MCF) is Amazon’s outsourced fulfillment service for merchants selling on non-Amazon sales channels, such as Chewy, whereby Amazon handles the picking, packing, and shipping of the orders coming from those sales channels.
Ecommerce Sellers can store their inventory at Amazon’s warehouses, and MCF will fulfill the non-Amazon orders from select channels. MCF deploys the same infrastructure and resources that power Amazon’s in-house Fulfilled By Amazon (FBA) logistics network.
ShipBob
ShipBob is a 3PL that focuses on serving ecommerce merchants. They have a nationwide network of order fulfillment centers that enable fast shipping, but they charge extra for guaranteed 2-day shipping. Built for ecommerce, they have an easy-to-use shipping software platform and a large set of pre-built integrations.
Cahoot: The Best Chewy 3PL
Selling on Chewy offers ecommerce businesses a powerful opportunity to reach millions of pet owners and expand into new markets. However, fulfilling Chewy orders comes with unique challenges, from meeting strict shipping expectations to navigating complex packaging and returns rules. Choosing the right Chewy 3PL partner is essential to ensure the channel contributes meaningful revenue growth with minimal babysitting.
Cahoot stands out as an ideal 3PL partner for Chewy merchants. With a large network of fulfillment centers and a focus on operational and cost efficiency (e.g., placing inventory closer to customers and using intelligent cartonization to keep shipping costs as low as possible), Cahoot ensures accurate order fulfillment and timely deliveries. Their commitment to customer satisfaction makes them a top choice for ecommerce businesses aiming to scale and succeed in the pet supply market. More specifically, their specialized Chewy 3PL services and deep understanding of the pet supply retailer’s platform make them the ideal partner to support your growth and profitability.
Summary
Table 1. Summary of the Chewy Marketplace Requirements
|
Requirement
|
Chewy Marketplace Drop-Ship Program Details
|
|---|---|
|
Access/Application
|
Invitation-only vendor program. Sellers are typically invited by a Chewy category manager or pitching through industry contacts. Onboarding is done through the Chewy Vendor Partner Portal (VPP). There is no public signup form.
|
|
Fees & Commission
|
Chewy does not publicly disclose marketplace commission or fee rates. (Anecdotal sources report vendors often face an ~18–19% “damage/compliance/marketing” fee on purchase orders, but official terms are not published.) Vendors invoice Chewy with net payment terms.
|
|
Payment Terms
|
Vendors are paid after order fulfillment. (Unofficial reports suggest Chewy pays ~60–90 days after receipt of goods, but official payment terms are not public.) Sellers can connect via ACH/bank account.
|
|
Integration/EDI/API
|
Mandatory integration via EDI or API. Chewy uses Rithum/DSCO: purchase orders (850) must use ANSI X12 v5010; other documents (ship notices, invoices, etc.) use v4010. Sellers can also use Rithum’s DSCO V3 API to sync orders, inventory, and shipments. Excel templates exist for initial inventory uploads.
|
|
Product Requirements
|
Sellers must provide complete product data (images, descriptions, UPCs) per Chewy’s specs. Drop-ship vendors skip Chewy’s “ordering info” steps (no warehouse addresses needed). Chewy publishes a “Drop-Ship Vendor Playbook” (via VPP) detailing SLAs, photo requirements, and packaging guidelines.
|
|
Shipping Expectations
|
Vendors ship orders directly to customers using premium carriers (typically FedEx, UPS, etc.). Chewy’s customer FAQ notes it does not ship to P.O. boxes or APO/FPO addresses, so sellers must ensure valid street addresses. Chewy pays customer shipping costs; vendors include shipping costs on their invoice. Vendors must meet Chewy’s fast-fulfillment SLAs (e.g., same/next-day pick, 1–3 or 1–5 days transit depending on category) as specified in the VPP playbook.
|
|
Packaging & Labels
|
Chewy requires branded packaging but does not use a traditional pack slip for drop-ship orders. Sellers should follow Chewy’s packaging instructions (available in VPP) and can include their own invoices or return forms. It’s recommended to include a Chewy shipping label and packaging that meets Chewy’s presentation standards.
|
|
Returns/Customer Service
|
Chewy offers a very generous return policy to customers (365-day free returns/refunds, per Chewy’s FAQs). In practice, Chewy only takes ownership of returned items once they reach Chewy’s fulfillment center. For drop-ship orders, Chewy typically processes refunds without requiring returned merchandise (unless Chewy requests it). Sellers should coordinate with their Chewy rep for any required return shipments. Chewy handles all customer support; vendors have a vendor support ticket system in VPP for disputes or product issues.
|
|
Shipping/Label Integration
|
Sellers must upload tracking info (often via EDI or VPP) when orders ship. Chewy provides shipping labels via its systems or integrations. Packages must meet dimensional and weight requirements (Chewy’s FAQ states a standard weight limit for FedEx Ground is 150 lbs) and include Chewy’s order ID on the carton.
|
|
Other Compliance
|
Sellers must follow Chewy’s policies (no extraneous marketing in boxes, no price tags). Chewy may require sellers to participate in marketing programs or advertising. Detailed compliance guidelines (including packaging barcodes, polybag requirements, etc.) are available in the Vendor Playbook on VPP.
|
If you’d like to find out how Cahoot can help your ecommerce business, please get in touch with us. We can’t wait to show you how Chewy order fulfillment was meant to be.

If you are selling on multiple sales channels and are interested in 3PLs that can help you with fulfillment, check out our other articles:
1. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Your Shopify Store
2. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Your Macy’s Orders
3. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Target Plus
4. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Wayfair
5. How to Choose the Best 3PL for Nordstrom
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Chewy a good platform for ecommerce retailers?
Chewy provides access to a large, loyal audience of pet owners who value convenience and fast shipping. This opens up new revenue streams and markets for ecommerce businesses.
What are the key challenges of fulfilling Chewy orders?
Sellers face strict packaging and shipping SLAs, complex returns processes, and the need for accurate inventory management to maintain customer satisfaction.
What should I look for in a 3PL for Chewy?
Look for expert knowledge of Chewy’s systems and requirements, efficient and ultra-fast fulfillment while containing costs, and proven capabilities in real-time inventory and order accuracy.
Why does logistics matter so much for Chewy orders?
Chewy’s customer experience hinges on fast, accurate deliveries. Logistics is critical to boosting customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term sales.
How can Cahoot help me fulfill Chewy orders?
Cahoot offers robust Chewy 3PL services, blending cutting-edge automation and transportation initiatives with real-time order fulfillment and responsive support, ensuring that your customers (and their pets!) are always happy.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

How AI Inventory Management Is Transforming Ecommerce Backoffice Systems
In this article
 8 minutes
8 minutes
Agentic AI, an emerging paradigm in artificial intelligence, emphasizes autonomy and decision-making capabilities in software systems. By enabling AI to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, agentic AI offers significant advantages in industries where efficiency, precision, and cost containment are critical. Its application in ecommerce is revolutionizing complex workflows, especially in order and inventory management, where speed and accuracy are essential for meeting customer expectations and fostering loyalty.
Order and Inventory Management Systems serve as the back office central nervous system for ecommerce businesses, handling product stocking, shipping, tracking, returns processing, customer service activities, and master product catalog maintenance. Integrating agentic AI into these systems enhances their ability to make real-time adjustments based on market fluctuations, predict consumer demand patterns, and optimize stock levels automatically. This reduces human error, streamlines workflows, and improves operational efficiency.
This combination of Agentic AI and Order and Inventory Management Systems marks a significant advancement beyond traditional automation. Leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI not only executes tasks but also analyzes data, predicts trends, and proactively optimizes business processes independently.
Let AI Optimize Your Shipping and Boost Profits
Cahoot.ai software selects the best shipping option for every order—saving you time and money automatically. No Human Required.
See AI in ActionIntroduction to AI in Inventory Management
AI in inventory management uses artificial intelligence technologies to automate and optimize inventory processes. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and other factors, AI predicts future demand and helps businesses maintain optimal inventory levels. This leads to improved operational efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
AI inventory management software employs machine learning and real-time data analysis to deliver valuable insights for demand forecasting, inventory tracking, and supply chain optimization. Continuous monitoring of inventory levels and data analysis enables businesses to meet customer demand while avoiding overstocking or stockouts, which optimizes cash flow.
The adaptability provided by AI enables businesses to respond effectively to market fluctuations and changing consumer behavior. This adaptability is essential for achieving and maintaining a competitive edge today.
Key Applications of AI
AI transforms inventory management through several key applications. Demand forecasting uses extensive historical data to accurately predict future demand, allowing businesses to adjust inventory levels to meet customer needs without excess stock.
Inventory optimization continuously analyzes stock levels to reduce carrying costs and minimize excess inventory, enhancing supply chain efficiency and generating significant cost savings and optimizing capital utilization.
Supply chain optimization benefits from real-time insights provided by AI, improving coordination across the supply chain, reducing delays, and boosting overall operational efficiency.
Additionally, AI automates routine tasks and provides actionable insights that drive business growth, enabling companies to operate more efficiently, lower costs, and improve customer satisfaction. This results in greater agility and competitiveness in the market. Let’s get a little more granular:
1. Demand Forecasting
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Agents are highly specialized applications built from a foundation of Large Language Models (LLM) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities (think ChatGPT or Llama by Meta AI), but instead of just returning an answer from a huge database of content built from webpages in the public domain, they can understand private, proprietary data and then “act” on the initial result to complete a workflow or achieve an outcome. The technology will transform how business operates across every sector. By integrating real-time Order and Inventory Management data with real-time news and events, AI agents predict demand with precision, enable real-time inventory tracking to enhance operational efficiency, automate customer service decisions and actions, help businesses maintain optimal inventory levels and improve inventory accuracy, remove waste from the fulfillment workflow, and finally enable a desirable returns solution. As ecommerce businesses embrace these advancements, they will not only streamline their operations but also build the agility needed to thrive in an increasingly complex and competitive industry.
2. Proactive Customer Support
AI agents can analyze customer data and purchase history to identify potential issues and proactively notify Sellers, (such as an order with a high likelihood of a return), and/or reach out to customers proactively to offer support and make changes to orders if needed (e.g. if an item runs small and the customer has returned similar items in a similar size). Further, they can provide automated outreach with personalized product recommendations, increasing customer satisfaction and sales.
3. Optimize Distributed Inventory Strategies
One of the biggest cost centers in ecommerce is shipping cost. Shipping is not free, nor has it ever been. Today’s retailers and brands are distributing inventory to 2 or more fulfillment centers to optimize delivery time and shipping cost. This is done by either opening and operating multiple warehouses, or partnering with a 3PL/4PL that can extend existing capabilities. AI agents can intelligently predict nationwide demand and create an accurate distribution plan to optimize placement and minimize the cost of transferring inventory between locations later.
ShipStation vs. Cahoot: 21x Faster, Real Results
Get the inside scoop on how a leading merchant switched from ShipStation to Cahoot—and what happened next. See it to believe it!
See the 21x Difference4. Optimize Fulfillment Cost and Workflows
Ecommerce merchants traditionally have humans use their experience to ship orders, but that approach is well known to be error-prone and contributes to higher fulfillment defect rates, and costs the company unnecessary capital to correct the mistakes (late delivery, shipped wrong item, etc.). Modern shipping software removes the human and creates the optimal shipping label that will deliver the order on time, every time. And now, combining that intelligence with AI agents, Order Management Systems (OMSs) can get even more granular and monitor weather conditions along shipping lanes, and then reroute orders to fulfillment centers that can deliver them by the promised delivery date, preventing a bad customer experience, and thus, limiting the likelihood of a return.
5. Make Returns Profitable
Ecommerce return rates have been steadily rising, often reaching 20–30% across the industry, and certain industries such as apparel, luxury goods, and electronics can see return rates as high as 40% or more as customers struggle to find the right fit without trying items on. It’s critical to manage returns effectively to retain as much revenue as possible and maintain a healthy bottom line. New AI-assisted returns technologies such as the Cahoot Peer-to-Peer Returns Solution are eliminating returns altogether by enabling the return to be shipped directly to the next customer, saving significant money and time for everyone.
Final Thoughts
Agentic AI is not just another incremental upgrade, it represents a paradigm shift in ecommerce operations. By entrusting routine yet complex back-office tasks to autonomous, data-driven agents, businesses unlock real-time responsiveness, razor-sharp forecasting accuracy, and seamless scalability. From anticipating demand surges to dynamic order routing and even transforming returns into revenue opportunities, AI-powered Order and Inventory Management Systems elevate efficiency and customer satisfaction in one fell swoop. As retail continues to evolve, companies that embrace agentic AI will gain the agility, cost savings, and strategic insights needed to stay ahead in an ever-more competitive landscape. The future of ecommerce back office systems is intelligent, proactive, and fundamentally human-centered, empowered by AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is “agentic AI”, and how does it differ from traditional AI in inventory management?
Traditional AI in inventory systems typically automates specific tasks, like sending low-stock alerts, based on predefined rules. Agentic AI goes a step further by making autonomous decisions and executing workflows end-to-end. In ecommerce back offices, that means AI agents can not only flag a potential stockout but also reorder, reassign inventory across warehouses, and even adjust pricing without human intervention, dramatically increasing speed and reducing manual errors.
How does AI-driven demand forecasting improve stock levels?
By ingesting historical sales data, real-time order volumes, market trends, and external factors (e.g., news, promotions), AI agents generate highly accurate short- and long-term demand predictions. This enables systems to automatically trigger restocks or redistribute inventory to regional fulfillment centers just before demand peaks, avoiding both costly overstocks and lost sales due to stockouts.
Can AI inventory management really reduce fulfillment costs?
Absolutely. AI agents analyze shipping lanes, carrier rates, and warehouse proximities to recommend the most cost-efficient fulfillment routes. For example, if bad weather threatens a shipping corridor, the system can reroute orders to a nearer fulfillment node, preventing delays and penalty fees. Over time, these continuous optimizations often shave several percentage points off overall fulfillment spend.
In what ways does AI enhance the returns process, and even make returns profitable?
Rising return rates can erode margins. AI-powered returns solutions (like peer-to-peer routing) direct unwanted items straight to another buyer rather than back to a central warehouse, saving transport and handling costs. They can also predict which orders are likely to be returned, based on sizing data or past customer behavior, and proactively offer exchanges or upsells before the return even happens, recouping revenue that might otherwise be lost.
How quickly can businesses see ROI after integrating AI into their OMS/IMS?
While results vary by scale and complexity, many merchants report measurable gains—5–15% reduction in carrying costs and a 10–20% improvement in on-time fulfillment performance—within 3–6 months of deploying agentic AI modules. Faster, error-free restocking alone can pay for the technology investment, and the compounding efficiency gains across customer support, shipping, and returns accelerate ROI further over time.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

The Ultimate Guide to Selling and Winning on Amazon Seller Fulfilled Prime
In this article
 31 minutes
31 minutes
- What is Seller Fulfilled Prime?
- SFP – Now More Relevant For Sellers Than Ever Before
- Diversify Beyond FBA
- Seller Fulfilled Prime – An Essential Tool for Ecommerce Growth
- The Competitive Advantages of Seller Fulfilled Prime
- Succeeding at SFP is Hard – Here’s Why
- The Cheat Sheet for Winning at Seller Fulfilled Prime
- Frequently Asked Questions
Watch On-Demand Webinar:
Amazon SFP – How To Sell and Win
In June 2023, Amazon announced they would reopen enrollment for their Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) program. Like most things in the Amazon world, the news was received with mixed reactions by Sellers. For those familiar with the Amazon ecosystem, they know that this program is challenging. Many feel the list of requirements is daunting and that Amazon holds them to higher standards than the ones it sets for its in-house Fulfilled By Amazon (FBA) logistics network.
Most people are familiar with the requirements that Amazon expects Sellers to meet, but far fewer are aware of the roadblocks that make success hard to achieve. An even smaller number are aware of the strategies they can deploy to meet Amazon’s criteria and surpass them. We’ve outlined all of that and more in our Ultimate Guide:
- We start by helping you understand what the program actually is and its benefits.
- Despite the daunting SFP requirements, the reward can be immense – we highlight the value that success in the program can deliver to your business.
- However, SFP success is not easy, and many Sellers find the program extremely challenging – we do a deep dive into the most common stumbling blocks that trip up even experienced Amazon merchants.
- Finally, we give you an essential cheat sheet needed to start selling and winning on Amazon Seller Fulfilled Prime!
One critical aspect to consider is the Seller Fulfilled Prime cost. Understanding the financial implications, including the program fee per item sold, percentage fees, and minimum fees, is essential for assessing potential profitability and managing profit margins effectively.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyWhat is Seller Fulfilled Prime?
Before we do a deep dive, it’s essential to understand – what is the Seller Fulfilled Prime program?
Definition and Benefits of Seller Fulfilled Prime
Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) is a program offered by Amazon that allows third-party Sellers to display the Prime badge on their listings while maintaining control over their fulfillment process. This means sellers can ship Prime orders directly to customers within two days, ensuring fast and reliable delivery. By participating in SFP, sellers can significantly boost their visibility, credibility, and sales potential, all while providing an enhanced customer experience.
The benefits of SFP include:
- Increased Visibility and Credibility: Listings with the Prime badge are more likely to be seen and trusted by customers.
- Greater Control: Sellers have more options and control over their fulfillment process and inventory management compared to using Fulfilled by Amazon (FBA).
- Brand Building: Sellers can build their brand, including flexibility to provide unique experiences for customers, such as custom packaging, while maintaining Prime status.
- Increased Sales and Profits: The Prime badge can lead to higher sales and better profit margins.
- Amazon’s Customer Service: Access to Amazon’s customer service and support for handling customer service inquiries, but the ability to own customer service if desired.
- Lower Fees: Freedom from the high fees associated with Amazon FBA.
- Improved Support for Challenging SKUs: The ability to meet the consumer expectation for free and fast shipping even on slow-moving, seasonal, larger-sized, and heavier SKUs.
While all these are great, the biggest one for any Seller is that the program allows your product listings on the Amazon Marketplace to feature the coveted Prime badge. With over 180 million subscribers in the United States in 2025, Amazon’s loyalty program has a great promise for the end customer – pay $139 (plus taxes) annually, and Amazon will deliver you stuff for free in under two days.
The program has far more profound implications for Sellers – their ranking on Amazon search results and ability to win the “Buy Box” is heavily and positively influenced by ensuring their products are Prime eligible. It’s also no secret that most shoppers on Amazon toggle the filter when browsing the store just to see products that qualify for Prime. All this means that an Amazon merchant’s survival, let alone success, largely depends on ensuring each SKU is Prime-eligible.
Seller Fulfilled Prime offers Sellers the best of both worlds – the Prime badge and autonomy over order fulfillment. However, it isn’t all smooth sailing, and Sellers have tended to shy away from the program because of its exacting standards. However, there are indications that the present time is a good one to begin seriously considering enrolling in the program.
“Cahoot has amazing technology in addition to their large warehouse network, sort of like FBA but without the hefty fees or restrictions. Cahoot saved our peak-selling season!”
~ Joel Frankel, Fames Chocolates
Speak to a fulfillment expert
How Seller Fulfilled Prime Works
To participate in SFP, sellers must meet Amazon’s stringent performance requirements. These include:
- Own Warehouse: Sellers must have their own warehouse, (or partner with a robust and capable modern 3PL), and an Amazon Professional Seller account.
- Premium Shipping Options: Offering premium shipping options to customers.
- Exceptional Performance Metrics: Consistently exceeds for the On-Time Delivery, Valid Tracking, and Delivery Speed metrics while maintaining a very low Order Cancellation Rate.
- Supported Carriers: Delivering orders with Amazon’s approved Seller Fulfilled Prime carriers.
- Amazon Returns Policy: Agreeing to the Amazon Returns Policy.
Sellers must also complete a trial period, during which they must fulfill at least 100 Prime packages while adhering to all of Amazon’s strict shipping requirements. Once the trial period is successfully completed, the Prime badge will be displayed on their listings, granting access to Prime customers. More on this later.
SFP – Now More Relevant For Sellers Than Ever Before
Several reasons have combined to make Seller Fulfilled Prime more relevant than ever before for Sellers, some of Amazon’s own making along with others that are not as palatable to the company:
The “Prime Effect”: Everybody Wants Fast Shipping
When Amazon first introduced Prime in 2005, it announced that it would ship customer orders over $35 for free in 2 days. At the time, people in the industry thought that the company had lost its mind and that this strategy would surely fail. It took competitors over a decade to offer free 2-day shipping – retailers like eBay and Walmart introduced their competing services only in 2017.
However, when Prime moved from its 2-day timeline to free 1-day shipping in 2019, Walmart and BestBuy responded almost immediately, offering customers the same experience. That captures just how much Amazon has raised the bar and redefined customer expectations – the Prime effect means that all of us expect everything delivered in under two days for free.
The stakes are high for ecommerce merchants across every channel – it does not matter whether you serve customers through a Shopify storefront, eBay, Amazon, or Walmart – you have to meet the consumer expectation for fast order fulfillment.
Shipping is no longer a back-office operation; it has become the defining element of the customer experience.
The company that created the Prime Effect is arguably the most customer-obsessed organization in the world. For years, Amazon has focused relentlessly on creating value for its customers – often at the expense of Sellers on its platforms. At every turn, the company has weaponized the size of its customer base and the network effects of its marketplace model to squeeze Sellers while delighting customers.
People, regulators, and governments aiming to call out the company on some of these practices have been met with a frequent refrain, “As long as the end customer is happy, how does it matter?” But why are customers so happy with Amazon, and how does the company have so many of them (most of whom are Prime members)? The most important reason is Amazon’s ability to ship products in under two days, nearly always on time.
“Cahoot allows us to offer 2-day shipping on our website in addition to driving more sales nationwide SFP on Amazon. This app saves us a ton of time and money every single day!”
~ OZ Medical
Speak to a fulfillment expert
Diversify Beyond FBA
For Sellers operating on Amazon, the approach has often been relatively straightforward: let Amazon FBA take care of it all and only use Fulfilled By Merchant (FBM) or SFP as a backup in the rare event of an emergency. However, given how FBA has repeatedly proven to quickly and substantially change program requirements and fees, a backup may no longer suffice – Sellers may need to devise an entirely new order fulfillment strategy.
Sellers Have Traditionally Relied on FBA
According to Jungle Scout, 64% of Amazon Sellers use FBA exclusively to deliver their orders, with only 14% choosing to completely cut ties with FBA and handle everything independently.
There are good reasons for this – the algorithm determining whether a product listing will win the Buy Box uses fast order fulfillment as a leading criterion. The fact that FBA listings are automatically Prime eligible is attractive for many Sellers (SFP listings also have a great chance to win the Buy Box, while merchant-fulfilled non-Prime orders trail well behind).
The well-known A10 algorithm, which ranks products in search results on Amazon, also prefers listings with fast order fulfillment, which has led Sellers to lean in heavily on FBA (again, a Seller Fulfilled Prime order can show up favorably, subject to the merchant doing other things right, such as optimizing for the right keywords in their product detail page copy).
The question Sellers might ask is: why would I do all the extra work required by SFP listings when it’s easier to win the buy box and rank well with FBA alone? To answer the question with a question: why not both? Not only do you get more shots on the Buy Box goal, but SFP listings typically sell for 15 – 20% more, plus increased discoverability and conversion compared to non-SFP FBM listings (82% of Sellers are offering both FBA and FBM versions of their listings).
So, why not all three? If you like FBA, continue to sell on FBA, but add SFP to your FBM listings and some will sell at the higher price and you’ve done nothing other than duplicate your listings. When the 180 Million Prime members apply the Prime-only filter when browsing for products on Amazon, they do it for no other reason than fast and free delivery. Will you be there to sell to them?
Seller Fulfilled Prime – An Essential Tool for Ecommerce Growth
Well, technically, you do have more to do than just duplicate your listings. You have to fulfill the orders with fast and free shipping, and you must meet the uncompromising performance metrics.
Seller Fulfilled Prime Requirements
- Maintain an On-Time Delivery Rate greater than 93.5% (A delivery is on time if it is delivered on or before the delivery date promised to the customer when they checkout).
- Maintain a Valid Tracking Rate (VTR) higher than 99% – a package has Valid Tracking if it has at least one carrier scan. This scan must occur before the package is delivered to ensure it provides a tracking number that can be used by the customer to track their order.
- Any product linked with a Prime shipping template must offer a minimum shipping speed of 3-5 days to the contiguous United States (the lower 48 states), across all 3 size tiers: Standard, Oversize, and Extra Large.
- Product detail page views must promise 1-day nationwide delivery to at least 30% of customers looking at Standard-size products, and 2-day nationwide delivery to at least 70% of page viewers of the same size tier. For Oversized products, these metrics are 10% and 45%, respectively. For Extra Large products, 15% of product detail page views must promise 2-day delivery (there is no 1-day expectation for these SKUs at this time). Note that Oversize and Extra Large SKUs may use regional shipping templates, so they are not required to deliver nationwide in 2 days or less.
- Merchants must first go through a pre-qualification process before starting their SFP trial. In the 90 days leading up to starting an SFP trial, they must self-fulfill at least 100 packages, with a Cancelation Rate <2.5%, Valid Tracking Rate >95% and Late Shipment Rate <4%. Once they are approved for the trial, they must ship at least 100 packages in 30 days while meeting all the SFP program requirements above.
- To fulfill Prime trial orders, Sellers should identify these orders within Seller Central by looking for the Prime badge and ‘IsPrime’ tag, which help in managing these specific orders efficiently.
- Sellers must provide free returns for all eligible items weighing less than 50 lb, for any reason.
- Amazon will not excuse late deliveries due to a carrier’s failure to deliver on time during the trial period (after passing the trial, they will). You must make sure that your order volume can incur a few late deliveries per trailing 7 days and still exceed the On-Time Delivery performance metric.
- During this entire period, the Prime badge will not be visible to customers on listings. After successful completion of the pre-qualification and trial period, Amazon will enable the Prime badge for your listings.
- You can request a 30-day SFP trial three (3) times per calendar year, and any trial overlapping the 30 days before major selling events such as Prime Day, Black Friday–Cyber Monday, or Christmas will be ineligible for graduation. Plan your trials in quieter months (e.g., January – February) to avoid wasted attempts.
- After graduating from the trial, you must fulfill a minimum 100 Prime-eligible packages each calendar month (evenly spread out) or face dynamic caps on your Prime order volume until you restore consistent output. It is not acceptable to ship 15 SFP orders in the first 3 weeks and then play catch-up in the last week; you will be throttled.
The critical thing to remember (which is the kick in the teeth for Sellers) is that Amazon FBA does not face any penalties for missing any of these performance metrics – whereas the onus is on the SFP merchant to diligently track these metrics and ensure you never fall below the minimums. To enable Prime shipping, Sellers must adjust their shipping templates and make specific selections in Seller Central to choose delivery regions for Prime service.
If this list appears daunting, you’re not alone – many Sellers feel these criteria are tough to meet. So before even looking at where the challenges and roadblocks lie, it’s worth asking – why is it worth being part of the program, and what value can it deliver to your business?
“Amazon SFP is such a demanding program, it is very difficult to find partners with the ability to pull this off. Cahoot is clearly geared towards Amazon Seller Fulfilled Prime, and excels at it via a network of strong fulfilment partners and a deeply knowledgeable team.”
~ Cali’s Books
Speak to a fulfillment expert
The Competitive Advantages of Seller Fulfilled Prime
While these are all great benefits for Sellers and provide their businesses with significant competitive advantages, making a success of the SFP program is highly challenging. Most merchants know that the requirements list is rigorous and demanding, but few are aware of the exact stumbling blocks that trip up people. Fewer are aware of solutions available to overcome these roadblocks and win at SFP.
Succeeding at SFP is Hard – Here’s Why
While the list of criteria is long and rigorous, we’ve identified the most challenging aspects of the program that trips up most Sellers:
Nationwide Fast Delivery Forces Most Sellers to Use Expensive Air Shipping
- In the past, Amazon had “regional Seller Fulfilled Prime” – which allowed Sellers to manage order fulfillment in certain geographical parts of the country while still having the Prime badge on their product listings.
- The Regional SFP program allowed merchants who owned a single warehouse or worked with a traditional 3PL with a single warehouse location to meet the program’s requirements through economical ground shipping.
- However, Amazon now expects Sellers to make products across every size tier available within 3-5 days (at the most) across the entire continental U.S. – additionally, approximately 70% of standard sized item orders must be delivered in under 2 days across the nation.
- The new requirements eliminate the possibility of regional models working any longer – having your inventory stationed in just one location means that shipments to certain parts of the country cross multiple shipping zones. The only way to deliver orders on time in such “single-node” operations is by using expensive air shipments. Making expensive shipments by air completely nullifies any cost savings merchants hoped to achieve when leaving FBA – in fact, it could worsen things.
- It becomes vital in such a scenario to use an SFP fulfillment partner with a strategically located network of fulfillment centers, such as Cahoot, whereby it is possible to cover the entire country in 2 days while still using economical ground shipping rather than express air shipments. Such a network is one of the very few ways it is still possible to both have nationwide coverage and significant cost savings over FBA.
- Lastly, Sellers must ensure that their product listings are classified correctly by Amazon. The metric for % of product detail pageviews that must promise a certain delivery speed is based on the size tier the item falls into (if an oversized or extra large item is classified as standard sized by mistake, you will be under pressure to get a large number of orders of those items delivered in under 2 days).
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPAmazon Expects Delivery in 2 Calendar Days, While Carriers Operate on Business Days
Amazon now expects Sellers to make Prime deliveries in 2 calendar days (necessitating the need to work with carriers that support weekend pickup and delivery). This requirement has caused Sellers a lot of pain and grief, and here’s why:
The Misleading Page Views Metric
In its latest round of revisions to the program criteria, Amazon has increased the percentage of product detail page views that must promise 1 calendar day and 2 calendar day delivery. Thirty-percent (30%) of product detail page views for standard sized products must promise 1-day delivery, while 70% must promise 2-day delivery. But when does your listing promise 1-day delivery, and when does it promise 2-day delivery? Let’s understand this with a few examples:
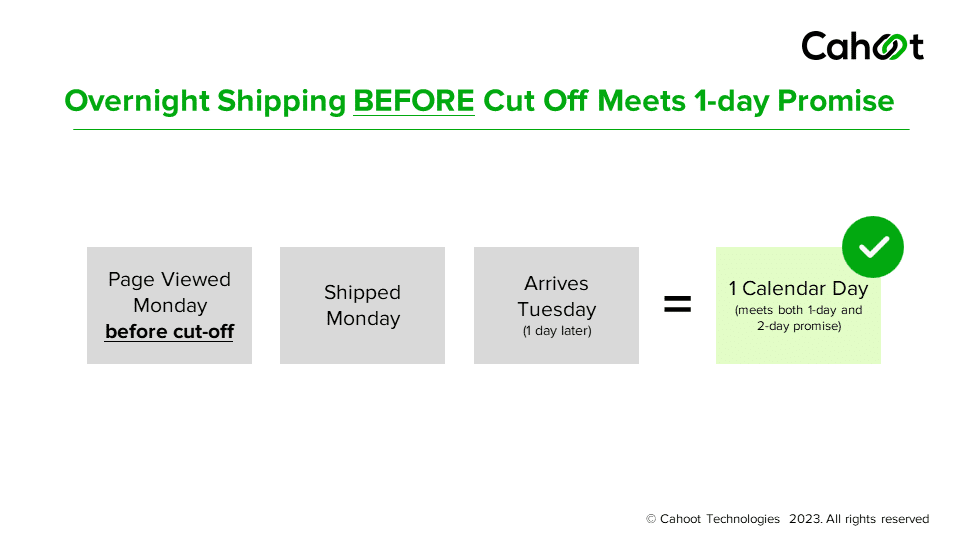
Let’s imagine every order is delivered the very next day after it ships. If a customer views your order on a Monday and places their order before the cutoff time, you will ship it that same day, and it reaches the customer the next day. In this case, Amazon displays a 1-day delivery promise and this page view counts towards your 1-day metrics.
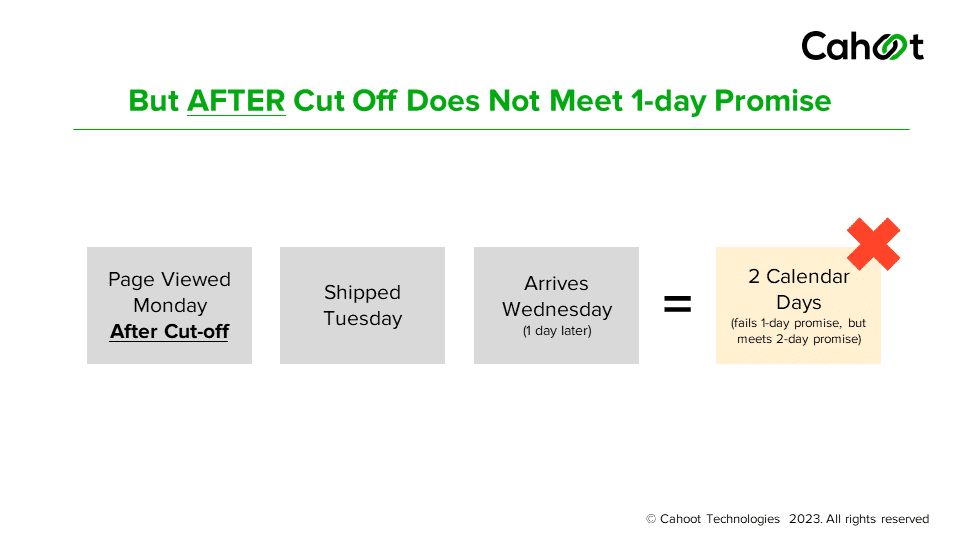
In this second case, when a customer looks at the product detail page after the cutoff time, you ship the order the next day after it is placed, and it reaches the customer the following day. This therefore fails to meet the 1-day promise, but meets the 2-day delivery promise (which means that if a 2-day promise was made after Monday’s order cutoff time, one-day shipping still needs to be used to deliver it in 2 calendar days).

In this last case, it gets really bad. If a customer views your listing on a Saturday evening, the item is expected to ship on Monday (assuming you don’t ship Sundays) and it will be delivered to them on Tuesday – a full 3 days later.
In this case, such a page view counts toward neither the 1-day nor 2-day metrics. The implication is clear – your listings will display 2-day and even 3-day delivery promises for significant periods of time. The mapping between the number of warehouses you have, the percentage of the US population you can service with 1-day delivery, and the % page views that actually promise 1-day delivery is not linear. This graphic illustrates that:
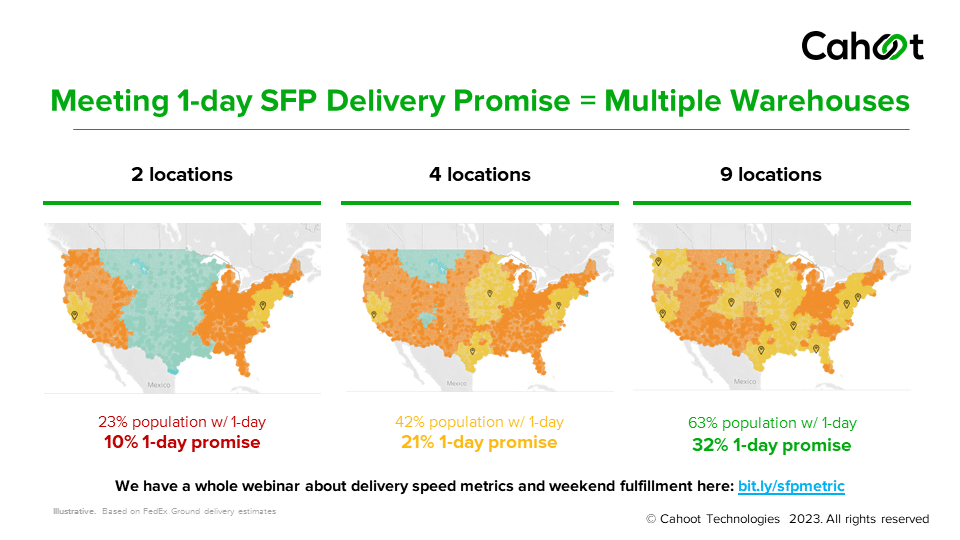
If you have warehouse locations, you can cover 42% of the US population with 1-day delivery. But different customers look at your product detail pages at different times of the day, and see different delivery speed promises. As per our research, in reality, only 21% of page views may actually promise 1 calendar day delivery. To meet the new Seller Fulfilled Prime delivery requirements, it could take as many as six to nine strategically located warehouses. These demanding metrics mean that traditional 3PLs will find it nearly impossible to help Seller Fulfilled Prime merchants (learn more about why traditional 3PLs are failing, and how peer-to-peer order fulfillment networks are designed to help you find success on SFP here). It becomes crucial for merchants to partner with order fulfillment networks that have warehouses at different strategic locations across the country, ensuring customers from anywhere see fast delivery promises. While merchants may want to upgrade to a fulfillment partner who is better positioned to meet these requirements, it’s easier said than done to leave your current 3PL for better alternatives. Many merchants don’t know how to evaluate and find the perfect fulfillment partner for them. If you’re looking for a step-by-step guide on migrating fulfillment partners, check out our guide here!
The Juggling Act Between Cut-off Times, Economical Shipping, and Meeting SLAs
With Seller Fulfilled Prime, a late cut-off time can potentially increase the number of orders your carrier picks up the same day, boosting your 1 and 2-day delivery metrics. If FBA faces any issues or does not meet the delivery promise shown to the customer on the product listing, there are no penalties for Amazon – but a Seller must meet the 93.5% on-time delivery criteria. Here’s a graphic demonstrating how delivery timelines look like when operating with a 2 PM cutoff time (based on our discussion of the page views metric):
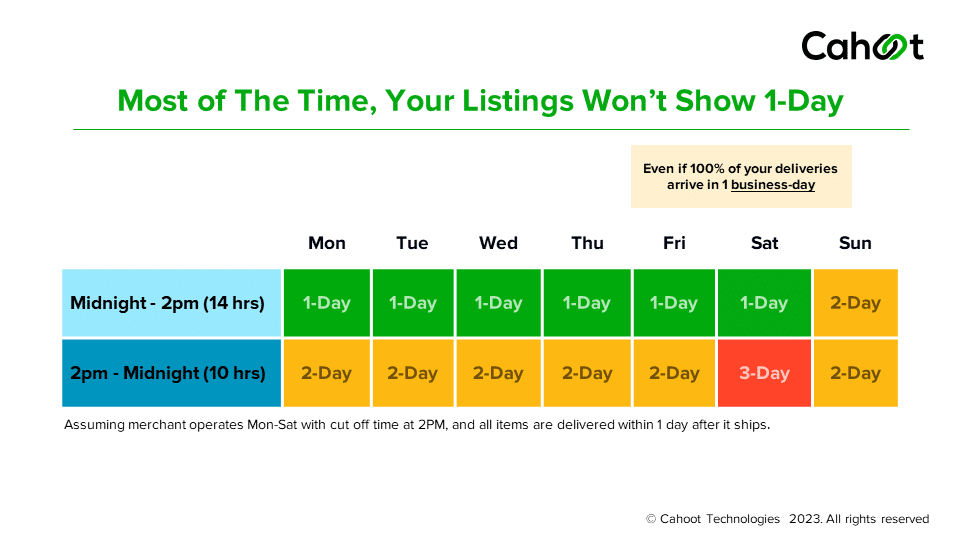
Sellers must carefully make the tradeoff between increasing their cutoff times (if they can schedule a late pickup with their carriers) versus also ensuring that those orders reach the customer the next day. Increasing the cutoff times increases the percentage of page views that promise 1 and 2-day delivery, but you must ensure that you can actually get the product to the customer’s doorstep within the time you’re promising. Here also, Sellers need to strategically place their inventory in a network of warehouses to avoid shipping orders placed close to cut-off times through expensive overnight air shipments. Placing inventory in different strategically located warehouses will enable nationwide coverage through economical ground shipping, all while meeting the customer’s expectations. Pay attention to time zones. A 2PM cutoff time is specific to the local time zone, so an order received before 5PM Eastern Time may need to ship from a western time zone to deliver on time, depending on the delivery promise. This makes it essential that your promotional activities (advertising, marketing) also closely follows the local time zones of the eyeballs you’re trying to reach. But it’s all very doable and Cahoot offers SFP consulting services to help. Reach out if you’d like to talk.
The shift to calendar days has had the most significant impact on the operational side of things – Sellers now have to plan a whole different way of running their business and schedules, which have also become challenges:
Operational Excellence Needed
Challenging to Staff And Operate Warehouses on Weekends
As we’ve mentioned before, staffing is often the biggest bottleneck towards finding success with order fulfillment. With weekend pick up and delivery expected to meet the calendar day-based SLAs, most merchants with a single warehouse or those working with 3PLs face difficulties succeeding in the program. If you own and operate your warehouses, paying your staff to work on the weekends or hiring additional people may eat into your margins to unfeasible extents. Traditional 3PLs, which are asset-heavy, also face cost pressures around labor – which they may be forced to pass onto Sellers. While these options erode any cost savings that Sellers see over FBA, you are not without alternatives – consider platforms like Cahoot, where each of our fulfillment centers is vetted for operational excellence and meets all the challenging requirements.
Arranging for Carrier Pickups on Weekends

In addition to warehousing, your carriers are another critical element in making your logistics work. Not all carriers offer weekend pick up and delivery – some may require you to be a large shipper and maintain minimum order volumes. All this means you may have to contact your account manager at the various carriers and enquire about possible options that may incur additional fees. However, while all this can be done, the biggest reason Sellers shy away from SFP is the heavy amount of process management, collaboration, and busy work needed to keep this operation running.
Managing Weekend Operations Can Overwhelm Sellers
It becomes easier to understand why so many Sellers shy away from Seller Fulfilled Prime – between working with multiple 3PLs to ensure your inventory covers the country, to operating and staffing your warehouses on the weekend as well as coordinating with your shipping carriers to arrange for weekend pickups, it can seem incredibly overwhelming and drain your bandwidth, time, and resources. You might often wonder whether managing so many stakeholders and sifting through so much busy work is worth it when FBA offers you only one party to work with – even if that party is Amazon, whose interests often tend to be misaligned with yours. It does not have to be this way – Sellers must spend time identifying partners who provide a unified experience where they get to work with just one vendor. Platforms like Cahoot help Sellers meet and exceed the SFP program requirement while ensuring you deal with only one company rather than coordinating between multiple 3PLs and carriers, preserving precious time and resources for you and your business.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkUnnecessary Surcharges From Amazon Buy Shipping
In its latest round of revisions, Amazon no longer mandates the use of its Buy Shipping platform to print shipping labels. This is a major relief for Sellers, because Amazon Buy Shipping comes with one major issue that they have reported anecdotally – the platform is not great at estimating the delivery timelines for USPS services (the comment below from Amazon’s Seller Central forums highlights the issue):

In many situations, Buy Shipping does not accurately estimate the delivery timeline within which a USPS service can make orders. In such cases, Sellers are faced with a choice to pick from two bad alternatives: fail to show the customer a fast delivery promise (not an option for SFP Sellers) or buy a more expensive label from the choices that Buy Shipping does believe are capable of meeting the SLA:

This can be tough for Sellers to swallow – as order volumes increase, the extra costs paid on each shipping label begin to mount, eroding margins and profitability. Thankfully, Amazon no longer requires the mandatory use of the service. However, this does not automatically mean that you will see increased savings. You still need to make sure that you’re picking the most economical label on every order! This requires technology like Cahoot’s next generation shipping software, which intelligently rate shops across all carriers and shipping services from all available warehouse locations to always print the cheapest label that will meet the delivery date promised to the customer.
So while a lot can potentially go wrong, Sellers can also make the program work for them and find success by following specific, vital strategies. Start finding success in the SFP program by using the tricks and recommendations in our SFP Cheat Sheet!
“Cahoot is a game-changer. Their fully automatic shipping label creation intelligently assigns the best carrier and shipping service for all my orders across all my channels.”
~ LoveOurPrices.com
Speak to a fulfillment expert
The Cheat Sheet for Winning at Seller Fulfilled Prime
To enable Prime shipping, sellers must adjust their shipping templates and make specific selections in Seller Central and add all the warehouse addresses orders will ship from to support delivery regions for Prime service.
- Achieve Nationwide Coverage With a Warehouse Network: Making orders nationwide in under two days is no easy task. You need to distribute inventory strategically in at least 6 different locations to cover 97%+ of the country in this window. Operating from a single warehouse or one or two 3PL fulfillment centers will simply not cut it – you need to distribute your products across a network to meet the program requirements economically.
- Use Data to Guide Inventory Placement And Avoid Air Shipping: Even with a network model, it is crucial to analyze where most of your orders are coming from – placing your inventory close to those “order hubs” becomes a vital part of ensuring you will meet and exceed the one and two-day delivery requirements. This also ensures that you can reach all of your customers through economical ground shipping rather than being forced to make too many expensive air shipments.
- Consolidate Relationships And Eliminate Busywork: SFP can lead you down the rabbit hole of investing in multiple 3PLs and coordinating with numerous carriers to make the program work for you. Sellers need to conduct research and identify a platform that provides a single relationship for you to manage – otherwise, logistics can overtake your focus on the activities that matter – selling and taking care of your customers.
- Save Every Dollar Across Every Shipment: The whole point of moving away from FBA towards a program like SFP is to extract cost savings. It is essential to align your technology towards automation, whereby you’re automatically generating the lowest price shipping labels on every single order.
- Monitor Metrics Like a Hawk: Amazon provides you with dashboards on Seller Central that provide all the SFP metrics needed. It is crucial to constantly stay on top of these and keep adjusting your strategy to ensure you’re meeting expectations.
- Appeals Process: You get 14 calendar days from notice to file, 4 days to respond to Amazon’s follow-up, and are limited to 3 appeals per quarter (successful appeals don’t count against your quota). Each appeal must include order IDs, scans, zip codes, and proof of any carrier delays.
Succeeding in this program is challenging, but we think these tips are a great place to start. As Q4 and the holiday season approach, now is the time for Sellers looking to diversify their order fulfillment beyond FBA and offer fast, profitable free shipping across every SKU to identify a partner who can help you win at Amazon Seller Fulfilled Prime. If you’d like to understand how Cahoot can be with you every step of the way, just fill out this form, and we’ll be in touch!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Seller Fulfilled Prime on Amazon?
Seller Fulfilled Prime allows you to list your products as Prime-eligible and handle the fulfillment yourself.
What is the difference between seller-fulfilled and Amazon fulfilled?
Logistics. Within the framework of Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), the platform handles the entire logistics process – from product storage in warehouses to dispatching. Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) leaves you 100% in charge of everything in this regard, yet forces you to cover dispatch fees at your own cost.
How do you pre qualify for the Seller Fulfilled Prime trial?
To pre-qualify for the Seller Fulfilled Prime trial you must meet the following criteria over the past 90 days: Self-fulfilled at least 100 packages, Cancellation rate less than 2.5%, Valid tracking rate greater than 95%.
What is the difference between SFP and FBA?
FBA offers scalability and customer trust but comes with higher costs and limited control. FBM provides cost savings and customization options but requires more time and effort. SFP combines Prime eligibility with control over costs but has stricter requirements and operational challenges.
Is Seller Fulfilled Prime worth it?
In reality, it’s more of a trade-off. Seller fulfilled Prime offers the advantage of the Prime Badge and lower fees than FBA, but Amazon also levies stricter, potentially more costly requirements than FBM. But SFP orders can command higher prices (15 – 20%) and allow for more control. With a well-managed program, it can be quite beneficial.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

Related Blog Posts
How to Use a Fulfillment Cost Calculator for DIY Estimates
In this article
 13 minutes
13 minutes
- Introduction to Fulfillment
- Fulfillment Centers and Costs
- Why 3PLs Can Offer a Cost-Effective Solution
- Understanding Fulfillment Fees
- Factors Affecting Fulfillment Costs
- Strategic Advantages of Partnering with a 3PL
- Comparing Costs and Potential Savings
- Best Practices for Fulfillment
- Why Partnering with a 3PL Makes Sense
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
Handling ecommerce order fulfillment in-house (DIY) often seems like the logical choice for businesses that want control over their operations. However, the true costs of a do-it-yourself (DIY) approach can quickly add up, and many of the expenses are not immediately obvious.
The most common in-house fulfillment costs include warehouse space, labor, packaging, shipping, and general operational overhead. Leasing or buying a warehouse, outfitting it with equipment like shelving, forklifts, pallet jacks, packing stations with computers and printers, plus covering utility bills, is just the beginning. On top of that, hiring, training, and managing employees to handle picking, packing, and shipping orders is a continuous commitment. Seasonal spikes in demand can make staffing both challenging and costly. Other factors, such as purchasing packaging materials and paying carrier fees, further contribute to the overall liability. Specific fees are often calculated based on estimates and rates applied by fulfillment companies.
Take a simple example: an ecommerce business processes 10,000 orders each month and spends $20,000 on rent, labor, and supplies. This puts the cost per order at $2. Adding an average shipping fee of $10 per package brings the total fulfillment cost to $12. If the average order value is $60, the cost of fulfillment alone eats up 20% of the sale price. These figures don’t even account for the cost of fulfillment defects, reverse logistics, software and technology investments, insurance, equipment maintenance, in-house or outsourced accounting staff, or the opportunity cost of time spent managing logistics rather than growing the business. Additionally, it’s important to estimate storage costs based on cubic feet for determining monthly expenses. Storage fees are typically applied monthly by 3PLs per cubic foot.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyIntroduction to Fulfillment
Fulfillment refers to the process of getting products from a warehouse to a customer’s doorstep, involving inventory management, packing, and shipping. It is a central aspect of ecommerce businesses, as it directly affects customer satisfaction and loyalty. Fulfillment costs, including warehousing, packaging, and shipping expenses, can significantly impact a business’s bottom line. Understanding fulfillment costs and fees is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about their logistics and supply chain management. A cost calculator can be a useful tool for estimating fulfillment costs and comparing prices among different fulfillment services.
Fulfillment Centers and Costs
Fulfillment centers are warehouses where products are stored, packed, and shipped to customers, and they can be operated by businesses themselves or outsourced to third-party logistics (3PL) providers. The costs of operating a fulfillment center can be significant, including expenses such as labor, equipment, and rent. Businesses should consider the costs and benefits of operating their own fulfillment center versus outsourcing to a 3PL provider. A fulfillment center can provide businesses with more control over their inventory and shipping, but it may also require significant investments in equipment, staff, and technology. The cost of shipping and handling can also vary depending on the location and capacity of the fulfillment center.
Why 3PLs Can Offer a Cost-Effective Solution
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers often outperform in-house fulfillment when it comes to cost-effectiveness. By working with many brands and retailers, 3PLs achieve economies of scale that most businesses can’t match. And while additional fees may apply for specific services such as protective packaging for fragile items and fees related to hazmat storage and peak season storage, they can be lower than your own costs, and may not even apply to you.
One key reason for their cost advantage is their strategically located warehouses. By positioning fulfillment centers near major cities, 3PLs can reduce shipping distances and “final mile” shipping costs. These providers also negotiate bulk shipping discounts with carriers, which aren’t typically available to smaller businesses shipping lower volumes. Savings also extend to shipping supplies, as 3PLs purchase mass quantities of boxes, mailers, and void fill in bulk and pass those lower costs on to their clients. Their pricing models offer full transparency, providing a clear breakdown of costs without overwhelming customers with complex pricing tables. Additionally, there are no hidden fees in 3PL pricing, ensuring customers pay only for the services they use.
Another benefit of 3PL partnerships is the advanced technology they typically use. Their systems are designed to streamline operations, from inventory management and order tracking to automated shipping processes that ensure fulfillment accuracy. For businesses managing fulfillment in-house, replicating these technologies would require a significant investment, not to mention the expertise needed to run them effectively.
For instance, let’s say an ecommerce business transitions from in-house fulfillment to a 3PL. If their DIY fulfillment cost per order was $12, a 3PL might offer the same service for $8 per order, thanks to better shipping rates and operational efficiencies. Over time, these savings add up substantially, and they only get better as businesses grow. Saving $4 per order across an average 10,000 orders per month is half a million dollars per year!
Understanding Fulfillment Fees
Fulfillment fees are charges associated with the processing and shipping of orders, and they can vary among different fulfillment service providers. These fees may include costs such as receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping, as well as additional services like returns processing and customer support. Businesses should carefully review the fulfillment fees and terms of their service provider to ensure they understand all the costs involved. A cost calculator can help businesses estimate their fulfillment fees and compare prices among different providers. It is essential to consider all the factors that affect fulfillment fees, including the type and weight of products, packaging materials, and shipping destinations.
Factors Affecting Fulfillment Costs
Fulfillment costs can vary depending on several factors, including the type and weight of products, packaging materials, and shipping destinations. Additional fees may apply for services such as gift wrapping, express shipping, or storage during peak seasons. The number of orders, units, and pallets can also impact fulfillment costs, as well as the level of customization required for packaging and shipping. Businesses should consider these factors when calculating their fulfillment costs and choosing a fulfillment service provider. A fulfillment fee is typically charged per unit or order, and it may include costs such as labor, materials, and shipping expenses.
Strategic Advantages of Partnering with a 3PL
Outsourcing fulfillment doesn’t just save money; it also provides strategic benefits that can help businesses expand and grow. One of the most significant advantages is the ability to scale fulfillment capacity up and down as volume changes. As an ecommerce business expands, for example, managing fulfillment in-house often requires more warehouse space, additional staff, and higher overhead costs. A 3PL, however, is already equipped to handle growth organically. Whether it’s a seasonal surge or a long-term increase in orders, 3PLs can adjust seamlessly to meet an ecommerce business’s needs.
Another advantage is faster and more efficient shipping, leading to faster and cheaper delivery to customers. Many 3PLs operate a nationwide network of fulfillment centers, allowing their clients to store inventory closer to their customers. This reduces transit times and shipping costs while improving customer satisfaction and encouraging loyalty and repeat business. Offering two-day delivery (or better) becomes much more feasible when orders are shipped from regional warehouses rather than a single central location. Additionally, 3PLs can cater to specific requirements, such as special storage conditions and packaging materials, ensuring customized services tailored for individual businesses.
Advanced technology integration is one more area where 3PLs excel. They make it easy to connect to, and support, omni-channel Sellers, automating order routing, distributed inventory management, tracking notifications, and even shipment exception visibility and handling. The risk of errors is diminished and visibility is enhanced with these technologies, saving businesses from having to manage customer service WISMO messages (“Where Is My Order?”), and decreasing the number of returned orders, letting them focus on other areas of their operation.
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPComparing Costs and Potential Savings
To decide whether outsourcing to a 3PL is the right move, businesses need to conduct a detailed review of their current costs and compare them to the estimates of what a 3PL would charge. This means tallying up all in-house expenses, including facilities, labor, storage, shipping supplies, and shipping postage, and then factoring in indirect costs such as time spent managing logistics, customer service, equipment costs (one-time and ongoing maintenance and supplies), and software.
Most 3PLs charge for receiving inventory, storage, picking and packing, materials, and shipping costs. While these fees might seem high at first glance, the savings they offer in carrier rates, packaging, and operational efficiencies often more than offset them. Businesses should also consider indirect savings like freeing up internal resources to focus on product development or marketing instead of logistics.
For example, a business spending $20,000 a month on in-house fulfillment might find that outsourcing to a 3PL reduces that figure to $14,000, saving $6,000. These savings can then be reinvested into growing the business or improving the customer experience (or taking a vacation). Over time, the reduced stress and increased operational efficiency that come with outsourcing ecommerce order fulfillment can have a big impact on the overall health of the business.
Use the table below to enter your monthly DIY order fulfillment costs and compare them to the average 3PL charges that can be expected from the average usage of each item. Make some assumptions, such as the number of hours spent on inventory prep, time spent on B2B operations, whether inventory will be shipped to a 3PL directly from suppliers or processed locally first, the cost of order fulfillment defects and subsequent returns, ergonomics, worker injuries, etc. The 3PL average costs below assume that products are standard size, as defined by Amazon FBA. Be sure to include all relevant details to get an accurate comparison.
|
Category
|
My Monthly Cost
|
3PLs Monthly Cost
|
|---|---|---|
|
Rent
|
|
NA
|
|
Labor
|
|
NA
|
|
Utilities
|
|
NA
|
|
Insurance
|
|
NA
|
|
Labor (Inventory Prep, Special Projects)
*3PL average: $42/hr |
|
|
|
Shipping Supplies
*3PL average: $0.40 – $1.25 per piece |
|
|
|
Shipping Postage
*3PL average: $8/shipment |
|
|
|
Customer Service
|
|
NA
|
|
Operations Management Time
|
|
NA
|
|
Equipment, Maintenance, & Supplies
|
|
NA
|
|
Software
*3PL average: $99/mo |
|
|
|
3PL Setup Fee
*3PL average: $0 – $999 |
NA
|
|
|
3PL Minimum Monthly
*3PL average: $49 – $499/mo |
NA
|
|
|
Receiving Fee
*3PL average: $42/hr |
|
|
|
Storage Fee
*3PL average: $0.56 – $0.89/ft3 |
|
|
|
Order Fulfillment Fee
*3PL average: $1.80 – $3.00/unit |
|
|
|
Returns Processing Fee
*3PL average: $2.99/unit |
|
|
|
Indirect Costs
|
|
NA
|
|
Total Costs:
|
|
|
Best Practices for Fulfillment
To optimize their fulfillment operations, businesses should consider implementing best practices such as streamlining their inventory management, using efficient packaging materials, and providing clear shipping instructions. It is also essential to monitor and analyze fulfillment costs and performance regularly to identify areas for improvement. Businesses should consider using a cost calculator to estimate their fulfillment costs and compare prices among different service providers. Providing excellent customer service and support is also crucial for building customer loyalty and trust. By following these best practices, businesses can improve their fulfillment operations, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkWhy Partnering with a 3PL Makes Sense
The decision to outsource fulfillment to a 3PL goes beyond cutting costs. It’s about positioning the business for long-term success. By working with a 3PL, businesses gain access to resources and expertise that would be expensive or impossible to build in-house. From advanced technology and strategic warehouse locations to robust carrier relationships, 3PLs provide the tools needed to compete in a complex ecommerce environment, with financial feasibility universally covered.
Outsourcing also allows businesses to focus on what they do best. Rather than worrying about packing boxes or negotiating with carriers, they can direct their energy toward areas that drive revenue, like creating new products or improving customer engagement and loyalty, which leads to increased customer lifetime value. In today’s interconnected world, partnering with a 3PL ensures that businesses can scale their operations globally, leveraging international logistical solutions and real-world data.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between in-house (DIY) fulfillment and outsourcing to a 3PL requires careful thought. While managing fulfillment internally offers control, it often comes with hidden costs and challenges that can limit growth. On the other hand, 3PLs may limit control, but they provide cost efficiencies that often reduce the overall cost of fulfillment operations while also supporting the ability to scale effortlessly with a pay-as-you-go model.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on a brand or retailer’s unique needs and goals. A wide range of services offered by 3PLs allows for customization and transparency in pricing based on specific business requirements. For many, partnering with a 3PL is the smarter move because it eliminates the mundane, routine work by offloading it to professionals at a predictable cost. By outsourcing fulfillment, businesses can save money, improve efficiency, and focus on what really matters: delivering exceptional value to their customers and boosting their ability to sell more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What expenses should I include when estimating DIY fulfillment costs?
When calculating in-house fulfillment costs, account for warehouse rent or mortgage; utilities; shelving, forklifts, and packing-station equipment; labor for picking, packing, and management; packaging materials; carrier fees; software subscriptions; insurance; and maintenance. Don’t forget indirect costs like returns processing, fulfillment errors, and the opportunity cost of time spent on logistics.
How do I calculate my cost per order for DIY fulfillment?
Tally your total monthly fulfillment expenses—rent, labor, supplies, and shipping postage—and divide by total orders processed. For example, $20,000 in monthly costs for 10,000 orders yields a $2 cost per order before shipping. Adding an average $10 shipping fee brings total fulfillment cost to $12 per order.
How can a 3PL provider lower my fulfillment costs?
3PLs leverage economies of scale: they negotiate bulk shipping discounts, purchase packaging in volume, and deploy strategically located warehouses to cut final-mile fees. Their advanced fulfillment technology automates inventory management and shipping, driving down per-order costs compared to a small-to-mid-sized business handling fulfillment internally.
What strategic advantages do 3PL partnerships offer beyond cost savings?
Outsourcing to a 3PL provides scalable capacity—seamlessly handling seasonal spikes without extra facility leases or staffing. A distributed network of fulfillment centers shortens transit times, enabling faster delivery and boosting customer satisfaction. Plus, integrated order-management systems reduce errors and free your team to focus on growth activities like marketing and product development.
How do I compare my DIY fulfillment costs to 3PL quotes?
Create a comprehensive cost model listing all in-house expenses: facilities, labor, supplies, software, and overhead. Then gather 3PL pricing for receiving, storage, pick & pack, materials, and shipping. Compare total monthly DIY vs. 3PL costs side by side—factoring in hidden savings like reduced WISMO customer inquiries and fewer returns—to determine the best fit for your business.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) & Premium Shipping Requirements Are Changing June 29, 2025: A Side-by-Side Deep Dive
In this article
 7 minutes
7 minutes
- Trial Enrollment & Graduation Windows for Seller Fulfilled Prime
- Monthly Volume & Enrollment Requirements
- Size-Tier Misclassification & Network Disruptions
- Appeals Process Overhaul
- OTDR Protection via Amazon-Managed Shipping Tools
- Premium Shipping Changes
- Putting It All Together: A Seller’s Checklist
- Final Thoughts
Starting June 29, 2025, Amazon is rolling out tighter performance guardrails for two of its marquee shipping programs: Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) and Premium Shipping. Seller Fulfilled Prime work refers to the process by which eligible third-party Sellers can fulfill Prime orders directly from their own warehouses, provided they meet Amazon’s strict performance requirements. For Sellers, these changes aren’t mere tweaks; they reshape how you qualify, stay in, and recover from hiccups in these programs. Below, we’ll walk through each key requirement as it stands today versus what you’ll need to hit after the effective date, with real-world examples to illustrate exactly what’s at stake. For a rundown of all program requirements, see the full Seller Fulfilled Prime Program and Premium Shipping policies.
Trial Enrollment & Graduation Windows for Seller Fulfilled Prime
Today:
- You can request a 30-day SFP trial any time.
- The SFP trial period lasts for 30 days and includes specific performance metrics that must be achieved to qualify for official enrollment in the program.
- Graduation from trial depends solely on meeting performance metrics during those 30 days.
After June 29:
- Three Trials Max per Year: You’ll be capped at 3 trial attempts in each calendar year. Any trial that begins before June 29, 2025 doesn’t count toward this limit.
- Quiet Periods Around Major Events: If your 30-day trial spans the 30 days leading up to Prime Days, Black Friday through Christmas, etc., you cannot graduate. This ensures Sellers are battle-tested before the busiest season.
Sellers must successfully complete the trial period by meeting specific performance requirements to gain access to Prime branding.
Why This Matters: Imagine you enroll in an SFP trial mid-October, aiming to graduate in time for Black Friday. Under the new rule, even flawless performance won’t earn you Prime status, you’ll have to re-enroll after the holidays. Plan your trials for quieter times (e.g., late January) to avoid losing a precious attempt.
Slash Your Fulfillment Costs by Up to 30%
Cut shipping expenses by 30% and boost profit with Cahoot's AI-optimized fulfillment services and modern tech —no overheads and no humans required!
I'm Interested in Saving Time and MoneyMonthly Volume & Enrollment Requirements
Today:
- There’s no fixed minimum monthly SFP volume.
- If you miss on-time metrics, Amazon sends warning emails, but your enrollment status remains until metrics severely degrade.
After June 29:
- Minimum 100 SFP Shipments/Month: You must deliver at least 100 Prime-eligible packages each calendar month, spread reasonably across weeks, to maintain the Prime badge.
- Dynamic Order Limits: Fall below 100 (or cluster all shipments in one week), and Amazon will impose a reduced daily Prime order limit until you return to consistent volume.
- Exemption for Fix-Ups: If you get a second warning for missing any metric, you can pause Prime (no shipments) for a week to get your house in order, and that period won’t count against your enrollment.
Practical Example: You shipped 15 Prime packages in the first 3 weeks of May, then scrambled to ship 90+ in the final week. In June, you’ll wake up to find your Prime orders capped at a fraction of normal volume. Better to target 25–30 SFP orders per week and build in some slack.
Size-Tier Misclassification & Network Disruptions
Today:
- Listing ASINs in the wrong size tier might trigger warning emails, but rarely leads to immediate suspension. Misclassification can also result in higher storage fees, impacting overall profitability.
- Late deliveries during huge storms or carrier outages may or may not be excluded automatically.
After June 29:
- Strict Misclassification Guardrails: Repeatedly offering a product under the wrong size-tier can lead to blocking of SFP offers or Prime status suspension/revocation for those ASINs.
- Automatic OTDR Exclusions for Major Disruptions: Clearer language confirms that any late deliveries from Amazon-identified large-scale carrier or weather events are excluded from your OTDR automatically.
Scenario: You classify a product as having larger dimensions to qualify for the less strict performance requirements that apply to a larger size tier. After three such mistakes, Amazon silently blocks Prime on that ASIN. You’ll need to correct the tier and appeal to restore it—costly downtime.
Appeals Process Overhaul
Today:
- You have a sliding window to dispute removals, but timelines and submission limits are vague.
After June 29:
- 14-Day Filing Window: From the date you receive a notice (e.g., “Your SFP status is paused due to low OTDR”), you have 14 calendar days to open an appeal.
- 4-Day Response to Requests: If Amazon asks for more details, you have 4 days to reply, or your appeal is closed.
- Limit of 3 Appeals/Quarter: You can file up to 3 appeals per quarter (overturned appeals don’t count). Appeals require supporting data (order IDs, tracking numbers, ZIP codes, proof of carrier delays).
Why It’s Tougher: Say your OTDR dips because a regional carrier hub froze over two days. You’ll need to create a case including tracking scans, carrier advisories, and order logs quickly, or forfeit that appeal.
Looking for a New 3PL? Start with this Free RFP Template
Cut weeks off your selection process. Avoid pitfalls. Get the only 3PL RFP checklist built for ecommerce brands, absolutely free.
Get My Free 3PL RFPOTDR Protection via Amazon-Managed Shipping Tools
Today:
- If you use Amazon Buy Shipping and meet delivery cut-offs, late deliveries often still count against you unless you separately request exclusions.
After June 29:
- “OTDR Protected” Labels: If you enable Shipping Settings Automation in your Prime templates and purchase “OTDR Protected” labels through Amazon Buy Shipping, any late deliveries on Standard (for SFP) or Premium shipping won’t hurt your OTDR.
- Continued Exclusion of Major Disruptions: Same carve-out for large-scale network events.
Bottom Line: Automate shipping profiles and purchase labels using Buy Shipping API, and you effectively get “insurance” against minor late-delivery slips.
Premium Shipping Changes
Amazon’s Premium Shipping program (items promised in 1–3 business days) gets its own tightening:
|
Requirement
|
Today
|
After June 29
|
|---|---|---|
|
OTDR Threshold
|
97%
|
93.5%
|
|
Measurement Window
|
Rolling 30-day period
|
Weekly (Sun–Sat)
|
|
Enforcement Steps
|
Removal upon sustained dip
|
3-strike system:
1st miss – warning email 2nd miss – warning email 3rd miss in 4 consecutive weeks – removal |
|
Warning Reset
|
None
|
4 consecutive perfect weeks clears prior infraction
|
Key Impact: Under the new cadence, a single bad week can put you on notice, and three such weeks in a month spells immediate removal from Premium Shipping. You’ll need more consistent performance throughout each month, not just a healthy 30-day aggregate. Sellers must successfully complete the new performance metrics to maintain their status in the Premium Shipping program.
Scale Faster with the World’s First Peer-to-Peer Fulfillment Network
Tap into a nationwide network of high-performance partner warehouses — expand capacity, cut shipping costs, and reach customers 1–2 days faster.
Explore Fulfillment NetworkPutting It All Together: A Seller’s Checklist
- Schedule Your SFP Trial Smartly: Avoid major sale seasons; plan for Q1.
- Lock Down 100+ Prime Shipments/Month: Automate your SFP orders to spread volume evenly across weeks.
- Clean Up Your ASIN Tiering: Audit listings for correct size tiers and package profiles.
- Enable Shipping Automation + Protected Labels: In Seller Central > Fulfillment Settings, turn on SFP/Premium templates and default to OTDR-protected labels.
- Monitor Weekly OTDR: Invest in an operations dashboard that can track your OTDR by week for both SFP and Premium orders.
- Prepare an Appeals Kit: Create a template for submitting an appeal with sections for order logs, tracking scans, and carrier advisories so you can file within 14 days. Cases created after 14 calendar days will not be considered.
- Build in Buffer for Disruptions: If a regional snowstorm hits, pre-notify Amazon to be considered for exemption from performance defects proactively. Consider outsourcing your SFP fulfillment to a distributed fulfillment network that organically solves for carrier network disruptions and ensures the highest performance metrics for continued program eligibility and enrollment.
- Understand SFP Program Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the stringent requirements of the SFP program and adapt to changing Amazon policies to maintain your SFP status.
Final Thoughts
These new Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) and Premium Shipping requirements underscore Amazon’s push for ultra-reliable, ultra-consistent delivery, a win for customers, and a heavier lift for Sellers. But by meeting these new standards, (whether independently or with the help of a distributed fulfillment network), Sellers can maintain access to Prime branding and the substantial customer base of Amazon Prime members, mitigating the risk to the sales opportunities afforded by the Amazon Seller Fulfilled Prime Program.
By understanding the before-and-after, planning trial timing, automating wherever possible (especially Prime shipping options), and building a rapid-response appeals process, you can not only stay enrolled in SFP and Premium Shipping programs but thrive in them.
Watch the Video

Turn Returns Into New Revenue

Related Blog Posts
How Ecommerce Returns Management Software Boosts Efficiency and Customer Loyalty
In this article
 9 minutes
9 minutes
- Why Returns Management Can’t Be an Afterthought
- What Returns Management Software Actually Does
- The ROI of Returns Management Solutions
- Why Reverse Logistics Matters
- Strategies for Reducing Returns
- Choosing the Right Returns Management Software
- Measuring Success: KPIs and Analytics for Returns Management
- My Perspective After a Decade in the Trenches
- The Future of Returns Management in Ecommerce
- Frequently Asked Questions
Returns used to be the messy backroom of ecommerce, hidden, clunky, and full of manual work. Not anymore. Commerce returns have emerged as both a major challenge and a significant opportunity for online retailers. In 2025, ecommerce returns management has become a strategic lever for customer loyalty, profit recovery, and operational speed. The importance of ecommerce returns management now extends beyond logistics, shaping competitive advantage and customer satisfaction in the digital age. After many years working with ecommerce brands and managing a distributed warehouse network, I’ve seen how the right returns management platform transforms what’s usually a pain point into a growth engine for both you and your customers.
Why Returns Management Can’t Be an Afterthought
Returns aren’t just a post-purchase nuisance. They are a customer experience touchpoint that directly affects customer lifetime value. The National Retail Federation reports that returns accounted for more than 17% of total retail sales in 2024. Return rates are even higher for online purchases compared to physical store sales, making a seamless returns process critical for ecommerce success. Every poor return experience risks losing customers, negative feedback, and lower repeat business.
I’ve seen merchants attempt to manage returns through spreadsheets and email threads, but it’s not scalable. The lack of a structured returns process and a clear returns policy leads to lost sales, inventory mismatches, refund delays, and angry customers by creating confusion and unmet expectations. Without the right returns management software, your customer service team spends hours just sending return labels and processing refunds manually.
Make Returns Profitable, Yes!
Cut shipping and processing costs by 70% with our patented peer-to-peer returns solution. 4x faster than traditional returns.
See How It WorksWhat Returns Management Software Actually Does
Good returns management software offers far more than a shipping label creation tool. It’s a comprehensive, all-in-one platform that automates and streamlines the entire process, from return authorization to inventory management and refund reporting. Key features typically include:
- Automated returns authorization to speed up approvals and reduce manual intervention.
- A customizable returns portal where customers can initiate and track their returns and exchanges.
- Self-service return portals that let online shoppers initiate returns without emailing support.
- Dynamic return rules for exchanges, store credit, or refunds, helping to protect profit margins.
- Streamlined returns processing to reduce support tickets and speed up the entire process.
- Real-time returns tracking functionality to keep both merchants and customers updated on return status.
- Automated exchange process options to encourage customers to swap products rather than request refunds.
- Automatic refunds processing capabilities to ensure timely and accurate refunds.
- Initiating refunds automatically once returns are approved, reducing manual errors.
- Real-time tracking of returns data, giving you insight into why products are being sent back.
- Integration with warehouse management systems ensures that inventory updates are instantly applied upon receipt.
- Fraud detection to combat return fraud and identify stolen merchandise patterns.
Merchants using returns management software often see customer satisfaction rise because the process is quick, transparent, and easy to navigate.
The ROI of Returns Management Solutions
A well-optimized returns management process offers key benefits that go beyond cost savings, including improved customer satisfaction, increased operational efficiency, and more revenue for your business.
Returns may feel like a cost center, but a well-optimized returns management process can actually increase revenue. How? By:
- Boosting customer loyalty with frictionless refunds and exchanges.
- Reducing reverse logistics expenses through automated label creation and bulk carrier discounts.
- Using returns data to improve product descriptions and reduce future returns.
- Recovering sales via store credit or streamlined exchange processes instead of one-click refunds.
- Retaining more revenue by minimizing unnecessary returns through efficient returns management.
From my experience, ecommerce businesses that prioritize customer satisfaction during the returns stage—by streamlining the process and offering easy-to-use return labels—see higher repeat business and better reviews. That translates to stronger brand loyalty, a healthier bottom line, and helps retain future customers.
Why Reverse Logistics Matters
The reverse logistics process—moving items from customers back to warehouses or physical stores—is more complex than most merchants realize. Without software, this process eats into profit margins and clogs warehouse management systems.
Modern returns management platforms integrate directly with inventory management tools, ensuring returned products are inspected, restocked, or flagged for disposal quickly. These integrations help maintain accurate inventory levels by seamlessly updating stock data during the returns process, preventing overselling or shortages. This saves time and prevents inventory from sitting idle, which otherwise delays future sales.
Offering unlimited returns—while once a popular strategy to attract customers—can create significant operational challenges for reverse logistics and inventory management due to increased processing costs and complexity.
Convert Returns Into New Sales and Profits
Our peer-to-peer returns system instantly resells returned items—no warehouse processing, and get paid before you refund.
I'm Interested in Peer-to-Peer ReturnsStrategies for Reducing Returns
Reducing returns is not just about protecting your bottom line; it’s about building trust and loyalty with your customers. For ecommerce businesses, a proactive approach to minimizing returns can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and streamline the returns process. One of the most effective strategies is to provide customers with comprehensive, accurate product information. High-quality images, detailed specifications, and authentic customer reviews help set clear expectations, reducing the chances of disappointment and unnecessary returns.
Another powerful tactic is to offer pre-sale consultations, such as live chat or virtual shopping assistance, to guide customers toward the right purchase. Post-sale follow-ups, like satisfaction surveys or helpful tips for product use, can address potential issues before they lead to a return. By making the returns process itself more transparent and user-friendly—through features like a self-service return portal and clear return policies—ecommerce businesses can further boost customer loyalty and reduce the volume of returns.
Ultimately, these strategies not only decrease return rates but also enhance customer satisfaction, turning first-time buyers into repeat customers and advocates for your brand.
Choosing the Right Returns Management Software
When evaluating a returns management solution for your online store, look for:
- Scalable features that match both current needs and future returns volume.
- Multi-channel support for both online returns and store returns.
- Customer communication tools to keep customers informed of their return status.
- Reporting capabilities for refund reports, product performance, and fraud analytics.
- Easy integration with your ecommerce platform and shipping carriers.
- Consider returns management software that offers free returns and free shipping options to enhance customer experience.
The best tools don’t just manage returns—they improve the customer experience, turning a negative moment into an opportunity to strengthen relationships. The right returns management solution can integrate with your store to streamline returns and exchanges.
Measuring Success: KPIs and Analytics for Returns Management
To truly optimize your returns management process, it’s essential to measure what matters. Ecommerce businesses should track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as return rate, reasons for return, customer satisfaction scores, and net promoter score. By analyzing returns data, you can uncover patterns, like which products are most frequently returned and why, which empowers you to make informed decisions about inventory management, product descriptions, and future product development.
For example, if returns data reveals that a particular item is often sent back due to sizing issues, you can update your sizing guides or add more detailed fit information to reduce future returns. Monitoring customer satisfaction throughout the returns process also helps identify pain points and opportunities to enhance the customer experience. Leveraging these analytics not only improves your returns management but also supports smarter business decisions, leading to higher customer satisfaction and increased revenue for your ecommerce business.
My Perspective After a Decade in the Trenches
I’ve seen brands waste thousands of dollars and countless hours on manual returns. Conversely, I’ve seen what happens when they adopt modern returns management software: faster processing, happier customers, and better informed decisions about product quality and operations.
Returns are often dismissed as unavoidable losses, but they’re actually a lens into your customer expectations, product quality, and operational gaps. Brands that treat returns as part of their customer experience strategy, rather than as an afterthought, see measurable lifts in customer lifetime value. Collecting and analyzing customer feedback is essential for continuously improving the returns process and ensuring it meets customer needs.
Even small changes, like offering free return shipping with a clear return policy, can dramatically improve repeat business. And when you combine those practices with a modern returns management platform, you’re not just reducing costs—you’re building long-term trust. Providing accurate product descriptions also helps reduce returns and strengthens customer trust.
No More Return Waste
Help the planet and your profits—our award-winning returns tech reduces landfill waste and recycles value. Real savings, No greenwashing!
Learn About Sustainable ReturnsThe Future of Returns Management in Ecommerce
Looking ahead, the future of returns management in ecommerce is all about delivering a seamless, customer-focused experience that drives both customer satisfaction and loyalty. As online shopping continues to expand, ecommerce businesses must prioritize efficient, transparent, and flexible returns processes to stay competitive. By investing in accurate product information, simplifying the returns process, and harnessing the power of returns data analytics, businesses can reduce return rates, improve operational efficiency, and foster long-term customer relationships.
Returns management software will play a pivotal role in automating and optimizing these processes, helping ecommerce businesses save time, reduce costs, and make data-driven decisions. Those who embrace a proactive, customer-centric approach to returns management will not only meet but exceed customer expectations, turning returns from a challenge into a strategic advantage. In the evolving world of ecommerce, prioritizing returns management is key to building customer loyalty, enhancing customer satisfaction, and driving sustainable business growth.
Returns are going to keep rising. The question is whether you’ll treat them as a competitive advantage or let them chip away at your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ecommerce returns management software?
It’s a comprehensive returns management solution designed to automate and streamline the returns process, from issuing return labels to tracking returned inventory and processing refunds or exchanges.
How does ecommerce returns management software boost customer satisfaction?
By providing a clear, fast, and self-service returns experience, customers feel informed and cared for. This improves overall trust and encourages repeat purchases.
Can ecommerce returns management platforms reduce costs?
Yes. Automation reduces labor hours, prevents errors, and cuts carrier costs by using bulk return labels and smarter reverse logistics routing.
Why is reverse logistics important?
Reverse logistics affects inventory turnover, customer wait times, and overall efficiency. Software ensures products move smoothly back into inventory or secondary channels.
Does Cahoot offer returns management capabilities?
Yes. Cahoot’s returns management tools integrate with ecommerce platforms and warehouse management systems, providing fast processing, cost savings, and actionable returns data.

Turn Returns Into New Revenue